A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALKALINE EARTH METALS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Practice sheet (Level-I(Main))|10 VideosALKALINE EARTH METALS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Practice sheet (Level-II(Advanced))|26 VideosALKALINE EARTH METALS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Lecture sheet (Level-I (Main))|10 VideosALKALI METALS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Questions for descriptive answers|17 VideosAROMATIC HYDROCARBONS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise OBJECTIVE EXERCIES - 3 (RECENT AIPMT/NEET QUESTIONS)|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH SERIES-ALKALINE EARTH METALS-Lecture sheet (Level-II (Advanced))
- Which salt hydrolyses to a minimum extent
Text Solution
|
- A doctor by mistake administres a dilute Ba(NO(3)) solution to a patie...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following statements (A) Gypsum contains a low percenta...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following are correct
Text Solution
|
- Which following are in correct
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following are correct
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements are false regarding BeCl(2)
Text Solution
|
- During setting of plaster of paris which of the following process take...
Text Solution
|
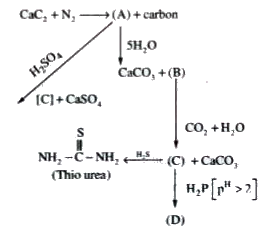
- 'A' is widely used as slow acting nitrogeneous fertilizer.
Text Solution
|
- 'B' is a weak basic aqueous NH(3) solution
Text Solution
|
- The compound 'C' is used to make urea and Thio urea.
Text Solution
|
- The compound 'D' is used as nitrogeneous fertilizer.
Text Solution
|
- The compound 'A' on heating gives a colourless gas and a residue. The ...
Text Solution
|
- The compound 'A' on heating gives a colourless gas and a residue. The ...
Text Solution
|
- The compound 'A' on heating gives a colourless gas and a residue. The ...
Text Solution
|
- Match the following columns
Text Solution
|
- Match the following columns
Text Solution
|
- The value of 'n' in the molecular formula Be(n) Al(2)Si(6)O(18) is
Text Solution
|
- When gypsum is heated at 393K, the compound formed is CaSO(4).XH(2)O v...
Text Solution
|
- How many of the following will turn moist red litmus blue and finally ...
Text Solution
|