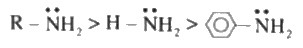Topper's Solved these Questions
GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Objective Exercise -1|204 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Objective Exercise -2|82 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Subjective Exercise -7|8 VideosENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise EXERCISE ON PASSAGE (PASSAGE-III)|5 VideosHYDROCARBONS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise ADDITIONAL PRACTICE SHEET ( LEVEL-II (PRACTICE SHEET (ADVANCED) (MATRIX MATCHING TYPE QUESTIONS)))|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH SERIES-GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-Subjective Exercise -8
- Phenol is more acidic than water and methanol is less acidic than wate...
Text Solution
|
- Acidic nature order of some alcohol is CH(3)OH gt CH(3)CH(2)OH gt (CH(...
Text Solution
|
- Relative strength of bases also can be explained by inductive effect
Text Solution
|
- Due to steric effect tertiary amines may not be more basic than second...
Text Solution
|
- Electromeric effect is the complete transfer of the shared pair of pi ...
Text Solution
|
- Electromeric effect is a temporary effect and comes into play instanta...
Text Solution
|
- When the transfer of electrons takes place towards the attacking reage...
Text Solution
|
- When the transfer of electrons takes place waya from the attacking rea...
Text Solution
|
- When both inductive and electronmeric effects simultaneously operate, ...
Text Solution
|
- Mesomeric or resonance effect is a permanent effect involving the tran...
Text Solution
|
- Electromeric effect always faciliates the reaction and never inhibits
Text Solution
|
- Groups with +M effect increase the electron density of the rest of the...
Text Solution
|
- Groups with -M effect decrease the electron density of the rest of the...
Text Solution
|
- Resonance effect is called conjugative effect if it is transmitted thr...
Text Solution
|
- The energy of actual structure of the molecule is lower than that of ...
Text Solution
|
- The difference between the real energy of the resonance hybrid structu...
Text Solution
|
- Resonance explains the stability of aromatic compounds, some unusual b...
Text Solution
|
- When alkyl groups are attached to an unsaturated system or a benzene n...
Text Solution
|
- Hyperconjugation is also called sigma-pi conjugation or no bond resoan...
Text Solution
|
- Grater the number of methyl groups attached to the double bonded carbo...
Text Solution
|