The resistive force acting on the oscillator in a fluid medium depends upon the velocity of the oscillator.
In practice, for not very large velocities, the resistive force is directly proportional to the velocity of the oscillator.
Resistive force `F_(d) propto -v`
`therefore F_(d) = -bv " "".........."(1)`
Where b is positive constant and it is called damping coefficient.
It depeds on characteristics of medium (like viscosity) and the size and shape of the block.
The unit of damping coefficient `(b =(F_d)/(v))" is "(NS)/(m)` and dimensional formula is `[M^(1)L^(0) T^(-1)]`.
When the oscillator has displacement x from mean position, the restoring force `(F_S)` produced in it is `F_(S) = -kx " ""......."(2)`
Thus, the total force acting on the mass at any time t is,
`F= F_(S)+ F_(d)`
`therefore F= -kx - bv " ""........."(3)`
If a(t) is the acceleration of mass at time t, then by Newton.s law of motion, `F= ma(t)`
From equation (3)
`ma(t) = -kx(t)- bv(t)" "".........."(4)`
but `a(t) = (d^(2)xk(t))/(dt^(2))" and "v(t) = (dx(t))/(dt)`
`therefore m(d^(2)x(t))/(dt^(2))+ b(dx(t))/(dt)+kx = 0" ""........"(5)`
is the differential equation for damping oscillations.
The solution of equation (5) is below (without proof)
`x(t) =Ae^(-(bt)/(2m)) cos [omega.t +phi]" ""........"(6)`
where `Ae^(-(bt)/(2m))` is the amplitude of oscillator and `omega.` is the angular frequency of oscillator and it is obtained from the formula `omega. = sqrt((k)/(m)-(b^2)/(4m^2))`
In this function, the cosine function has a period `(2pi)/(omega.)` but function x(t) is not pure periodic because of the factore `e^(-(bt)/(2m))` which decreases continuously with time. If the decrease is small in one time period T, the equation (6) is approximately periodic.
The solution of equation (5) can be graphically represented as shown in figure.
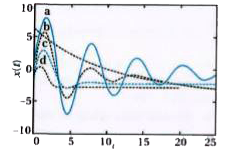
Equation (6) is considered as consine function whose amplitude `(Ae^(-(bt)/(2m)))`, which is gradually decrease with time.
In the graph a damped oscillator is periodic with decreasing amplitude of oscillation with greater damping oscillation die out faster.
