For small damping and `omega_(d)b lt lt m(omega^(2)-omega_(d)^(2))` then `omega_(d)b` is neglected compared to `m(omega^(2)- omega_(d)^(2))`
Amplitude of damped oscillation `A= (F_0)/(m(omega^(2)-omega_(d)^(2)))` and for `omega= omega_(d)` amplitude is `A= (F_0)/(omega_(d)b)`.
Below figure shows the dependence of the displacement amplitude of an oscillator on the angular frequency of the driving force for different amount of damping present in the system.
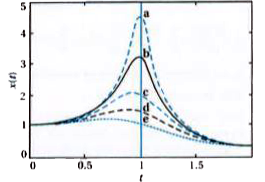
The curves in this figure show that, if we go on changing the driving frequency `(omega_d)`, the amplitude tends to infinity when it equal to the natural frequency `(omega)`. But this the ideal case of zero damping which never arises in a real system because the damping is never perfectly zero.
The curves for amplutude `(omega)/(omega_0)` corresponding to different value of b are shown in figure.
The amplitude becomes infinite for `omega_(d)= omega` when b=0. As damping increases, the value of maximum amplitude in graph displaced towards left side.
