Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
OSCILLATIONS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-D (NCERT EXEMPLAR SOLUTION LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS)|8 VideosOSCILLATIONS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-E (MCQs ASKED IN GUJARAT BOARD AND COMPETITIVE EXAMS)|66 VideosOSCILLATIONS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-D (NCERT EXEMPLAR SOLUTION VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS)|10 VideosOBJECTIVE QUESTIONS AS PER NEW PAPER STYLE
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise CHAPTER - 8 (Match Type questions)|5 VideosPHYSICAL WORLD
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-E (QUESTIONS FROM MODULE)|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-OSCILLATIONS-SECTION-D (NCERT EXEMPLAR SOLUTION SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS)
- Find the time period of mass M when displaced from its equilibrium pos...
Text Solution
|
- Show that the motion of a particle represented by y= sin omega t- cos ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the displacement of a simple harmonic oscillator at which its PE ...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass m is situated in a potential field U(x)= U(0) (1-cos al...
Text Solution
|
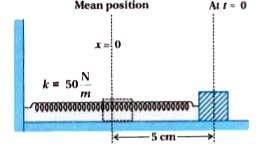
- A mass 2kg is attached to the spring of spring constant 50 Nm^(-1). Th...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a pair of identical pendulums, which oscillate with equal amp...
Text Solution
|