Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
OSCILLATIONS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-E (MCQs ASKED IN GUJARAT BOARD AND COMPETITIVE EXAMS)|66 VideosOSCILLATIONS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-F (QUESTIONS FROM MODULE SIMPLE QUESTIONS)|20 VideosOSCILLATIONS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-D (NCERT EXEMPLAR SOLUTION SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS)|6 VideosOBJECTIVE QUESTIONS AS PER NEW PAPER STYLE
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise CHAPTER - 8 (Match Type questions)|5 VideosPHYSICAL WORLD
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-E (QUESTIONS FROM MODULE)|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-OSCILLATIONS-SECTION-D (NCERT EXEMPLAR SOLUTION LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS)
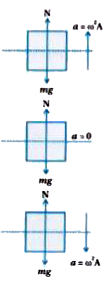
- A person normally weighing 50kg stands on a massless platform which os...
Text Solution
|
- A person normally weighing 50kg stands on a massless platform which os...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass m is attached to one end of a massless spring which is ...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass m is attached to one end of a massless spring which is ...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical log of wood of height h and area of cross-section A floa...
Text Solution
|
- One end of V-tube containing mercury is connected to a suction pump an...
Text Solution
|
- A tunnel is dug through the centre of the earth. Show that a body of m...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum of time period 1s and length l is hung from a fixed ...
Text Solution
|