A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
OSCILLATIONS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-F (QUESTIONS FROM MODULE SIMPLE QUESTIONS)|20 VideosOSCILLATIONS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise QUESTION PAPER (SECTION - A)|6 VideosOSCILLATIONS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-D (NCERT EXEMPLAR SOLUTION LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS)|8 VideosOBJECTIVE QUESTIONS AS PER NEW PAPER STYLE
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise CHAPTER - 8 (Match Type questions)|5 VideosPHYSICAL WORLD
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-E (QUESTIONS FROM MODULE)|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-OSCILLATIONS-SECTION-E (MCQs ASKED IN GUJARAT BOARD AND COMPETITIVE EXAMS)
- A horizontal surface moves up and down in SHM with an amplitude of 1 c...
Text Solution
|
- A particle executes SHM of period T and amplitude l along a rod AB of ...
Text Solution
|
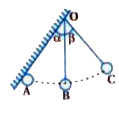
- A ball is suspended by a thread of length L at the point O on a wall w...
Text Solution
|
- Let T(1)" and "T(2) be the time periods of spring A and B when mass M ...
Text Solution
|
- In the equation of motion of waves in x-direction is given by y= 10^(-...
Text Solution
|
- Total energy of SHM particle…….
Text Solution
|
- Two springs of spring constant k(1)" and "k(2) are joined in series. H...
Text Solution
|
- Two simple harmonic motion are represented by the equation y(1)= 0.1 s...
Text Solution
|
- The circular motion of a particle with uniform speed is…………
Text Solution
|
- A silver atom in a solid oscillaties in simple harmonic motion in some...
Text Solution
|
- A simple harmonic motion of a particle is represented by an equation x...
Text Solution
|
- A mass M is suspended from a spring of negligible mass. The spring is ...
Text Solution
|
- A simple harmonic motion of a particle is represented by an equation x...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m be placed on a frictionless surface of a table. Spri...
Text Solution
|
- Acceleration of a particle a= -bx, where x is the displacement of part...
Text Solution
|
- A mass m suspended at the end of spring of spring constant k and oscil...
Text Solution
|
- The displacement of a particle performing SHM x= 3sin 2t+4 cos 2t. The...
Text Solution
|
- A body is moving in a room with velocity 20 m"/"s perpendicular to the...
Text Solution
|
- A lift is ascending with acceleration (g)/(3). Find the time period of...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of maximum velocity and maximum acceleration of a particle o...
Text Solution
|