Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CURRENT ELECTRICITY
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION [B] (NUMERICAL)|10 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION C NCERT EXEMPLAR SOLUTION (MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs))|6 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION [B] (NUMERICAL FROM TEXTUAL EXERCISE)|35 VideosBOARD'S QUESTION PAPER MARCH-2020
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise PART-B SECTION -C|4 VideosDUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section-D (MCQs asked in GUJCET/Board Exam)|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-CURRENT ELECTRICITY-SECTION [B] (NUMERICAL FROM .DARPAN. BASED ON TEXTBOOK)
- The current through a wire varies with time as I = I(0) + alpha t , ...
Text Solution
|
- Two materials have the value of alpha(1) and alpha(2) as 6 xx 10^(-4) ...
Text Solution
|
- A cube is constructed by connecting 12 wires of equal resistance as sh...
Text Solution
|
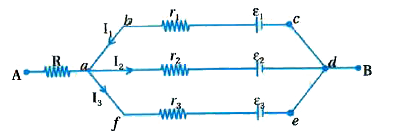
- In the circuit shown in figure, epsilon(1) = 3 V, epsilon(2) = 2 V ,...
Text Solution
|
- 200 Omega resistor is connected in one of the gaps of the meter bridge...
Text Solution
|
- An n-type semiconductors has 4 xx 10^(-3) m width, 25 xx 10^(-5) m t...
Text Solution
|
- The emf of the batteries E, F, G and H are 2 V, 1 V, 3 V and 1 V respe...
Text Solution
|
- A and B are two electric bulbs with their ratings respectively 40 W, 1...
Text Solution
|
- At temperature 0""^(@) C and 100 ""^(@) C, currents passing through o...
Text Solution
|
- If deflection in galvanometer in above circuit is zero then find value...
Text Solution
|
- Five resistor each having value of 4 Omega are connected with ideal ba...
Text Solution
|
- In one part of above network, steady current is flowing. Values of res...
Text Solution
|
- Resistance of 100 cm long potentiometer wire is 10Omega. It is connect...
Text Solution
|