Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section-D (multiple choice questions (MCQs)|48 VideosDUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section-D (multiple choice questions (MCQs) (photo-electric effect)|1 VideosDUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section-C (Very short answer type questions)|11 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION [D] MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs) (MCQs ASKED IN BOARD EXAM AND GUJCET)|23 VideosELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION D MCQS ASKED IN COMPETITIVE EXAMES (MCQS AKSED IN BOARD EXAM AND GUJCET)|14 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER-Section-C (Long answer Type Question)
- Consider a thin target (10^(-2) m square ,10^(-3) m thickness) of sodi...
Text Solution
|
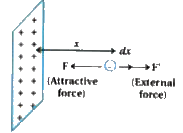
- Consider an electron in front of metallic surface at a distance d(trea...
Text Solution
|
- A student performs an experiment on photoelectric effect,using two mat...
Text Solution
|
- A particle A with a mass m(A) is moving a velocity v and hits a partic...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a 20 W bulb emitting light of wavelength 5000 Å and shining o...
Text Solution
|