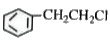A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Aliphatic nucleophilic substitution mainly takes place by two mechanis...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following alkyl halides mainly undergo reaction by SN^2 m...
Text Solution
|
- Aliphatic nucleophilic substitution mainly takes place by two mechanis...
Text Solution
|
- Aliphatic nucleophilic substitution mainly takes place by two mechanis...
Text Solution
|
- SN^2 reactions of alkyl halides is a bimolecular reaction which take p...
Text Solution
|
- SN^2 reactions of alkyl halides is a bimolecular reaction which take p...
Text Solution
|
- Nucleophilic substitution reactions are of two types, substitution nuc...
Text Solution
|
- Nucleophilic substitution reactions are of two types, substitution nuc...
Text Solution
|
- Nucleophilic substitution reactions are of two types, substitution nuc...
Text Solution
|