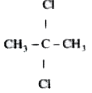
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- In the study of chlorination of propane four products (A,B,C and D) (s...
Text Solution
|
- In the study of chlorination of propane, four prouducts A, B, C, and D...
Text Solution
|
- In the study of chlorination of propane, four product (A,B & C,D) of t...
Text Solution
|
- In the study of chlorination of propane, four product (A,B & C,D) of t...
Text Solution
|
- In the study of chlorination of propane, four product (A,B & C,D) of t...
Text Solution
|
- In the chlorination, substitution reaction of propane two isomeric pro...
Text Solution
|
- In the Chlorination, substitution reaction of propane, two isomeric pr...
Text Solution
|
- In the chlorination, substitution reaction of propane, two isomeric pr...
Text Solution
|
- In the syudy of cholrinatio of propane , four products (A,B Cand D of ...
Text Solution
|