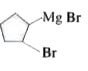
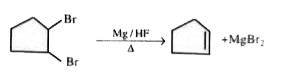
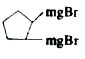A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- R - X + Mg overset("ether". Delta)(to) overset(delta-)( R) - overset(d...
Text Solution
|
- Grignard reagent is usually prepared by R-X+Mg overset(Et(2)O)rarrRM...
Text Solution
|
- Grignard reagent is usually prepared by R-X+Mg overset(Et(2)O)rarrRM...
Text Solution
|
- R-X+Mgoverset(Ether,Delta)rarroverset(delta-)R-overset(delta+)Mg-X Gri...
Text Solution
|
- R-X+Mgoverset(Ether,Delta)rarroverset(delta-)R-overset(delta+)Mg-X Gri...
Text Solution
|
- Alkane may be prepared from alkyl hlide by Wutrtz method where alkyl h...
Text Solution
|
- Grignard reagents (RMgX) are prepared by the reaction of an organic ha...
Text Solution
|
- Grignard reagents (RMgX) are prepared by the reaction of an organic ha...
Text Solution
|
- Grignard reagents (RMgX) are prepared by the reaction of an organic ha...
Text Solution
|