Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
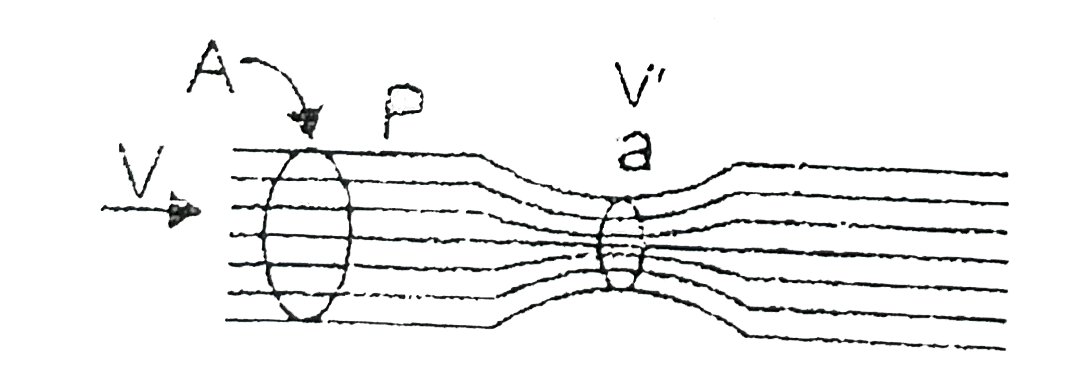
- Consider the Venturi tube of Figure. Let area A equal 5a. Suppose the ...
Text Solution
|
- Can pressure (p) ,density (p) and velocity (v) be taken as fundunental...
Text Solution
|
- The mass of the liquid flowing per second per unit area of cross secti...
Text Solution
|
- Water flows with a velocity V in a tube of diameter d and the rate of ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the Venturi tube of Figure. Let area A equal 5a. Suppose the ...
Text Solution
|
- The rate of steady volume flow of water through a capillary tube of le...
Text Solution
|
- एक असमान परिच्छेद वाली क्षैतिज नली में जल बह रहा है । किन्ही दो स्थानो...
Text Solution
|
- एक क्षैतिज नली में जल धारा-रेखी प्रवाह में बह रहा है । नली में किसी बि...
Text Solution
|
- Water is flowing streamline motion through a horizontal tube. The pres...
Text Solution
|