Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH-ELECTROCHEMISTRY-All Questions
- Write the cell reaction of a lead storage battery when it is discharge...
Text Solution
|
- Why on dilution the Lambda(m) of CH(3)COOH increases drastically, whil...
Text Solution
|
- Match the terms given in column I with the units given in column II.
Text Solution
|
- Match the terms given in Column I with the items given in Column II. (...
Text Solution
|
- Match the items of Column I and Column II.
Text Solution
|
- Match the items of Column I and Column II.
Text Solution
|
- Match the items of Column I and Column II.
Text Solution
|
- Match the items of Column I and Column II on the basis of data given b...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion(A) Cu is less reactive than hydrogen. Reason(R) E(Cu^(2+)/...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) E("cell") should have a positive value for the cell to f...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) Conductivity of all electrolytes decreases on dilution. ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion(A) Lambda(m) for weak electrolytes shows a sharp increase wh...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion(A) Mercury cell does not give steady potential Reason (R) ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion(A) Electrolysis of NaCl solution gives chlorine at anode ins...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion(A) For measuring resistance of an ionic solution an AC sourc...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion(A) Current stops flowing when E("cell")=0 . Reason(R) Equi...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion(A) E(Ag^(+)//Ag^(@) increase with increase in concentration ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) Copper sulphate can be stored in zinc vessel. Reason(R...
Text Solution
|
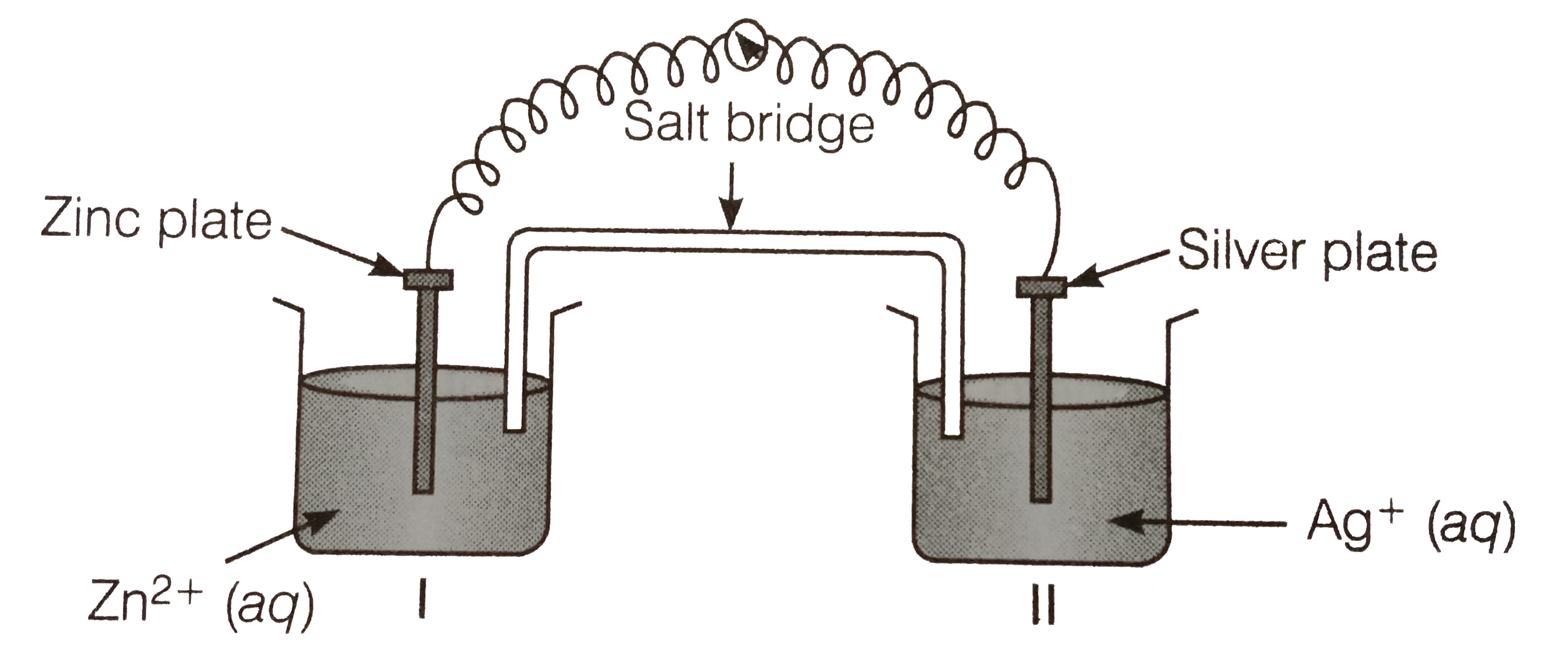
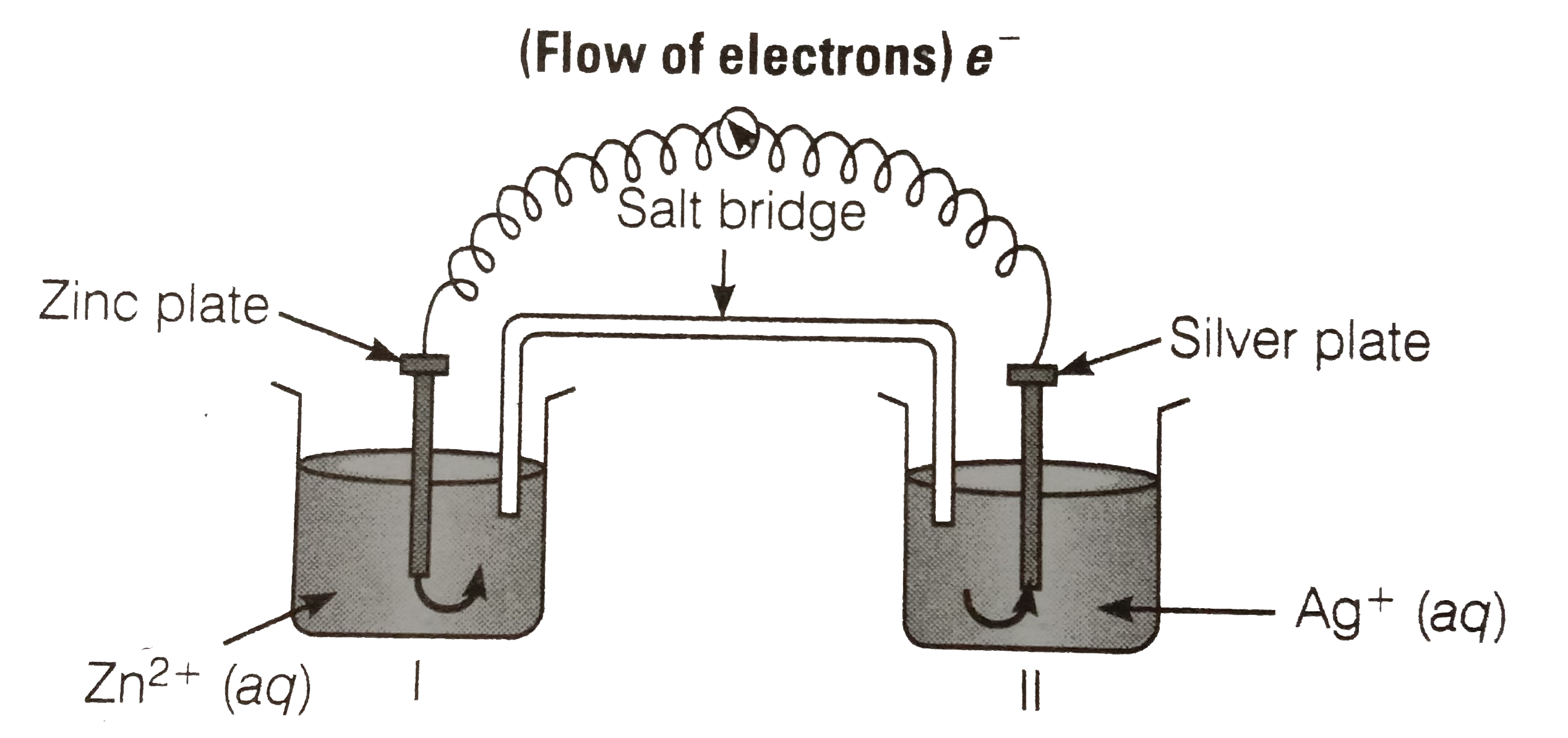
- Consider the figure and answer the following question. (i) Cell '...
Text Solution
|
- Consider figure from the above question and answer the questions (i) t...
Text Solution
|