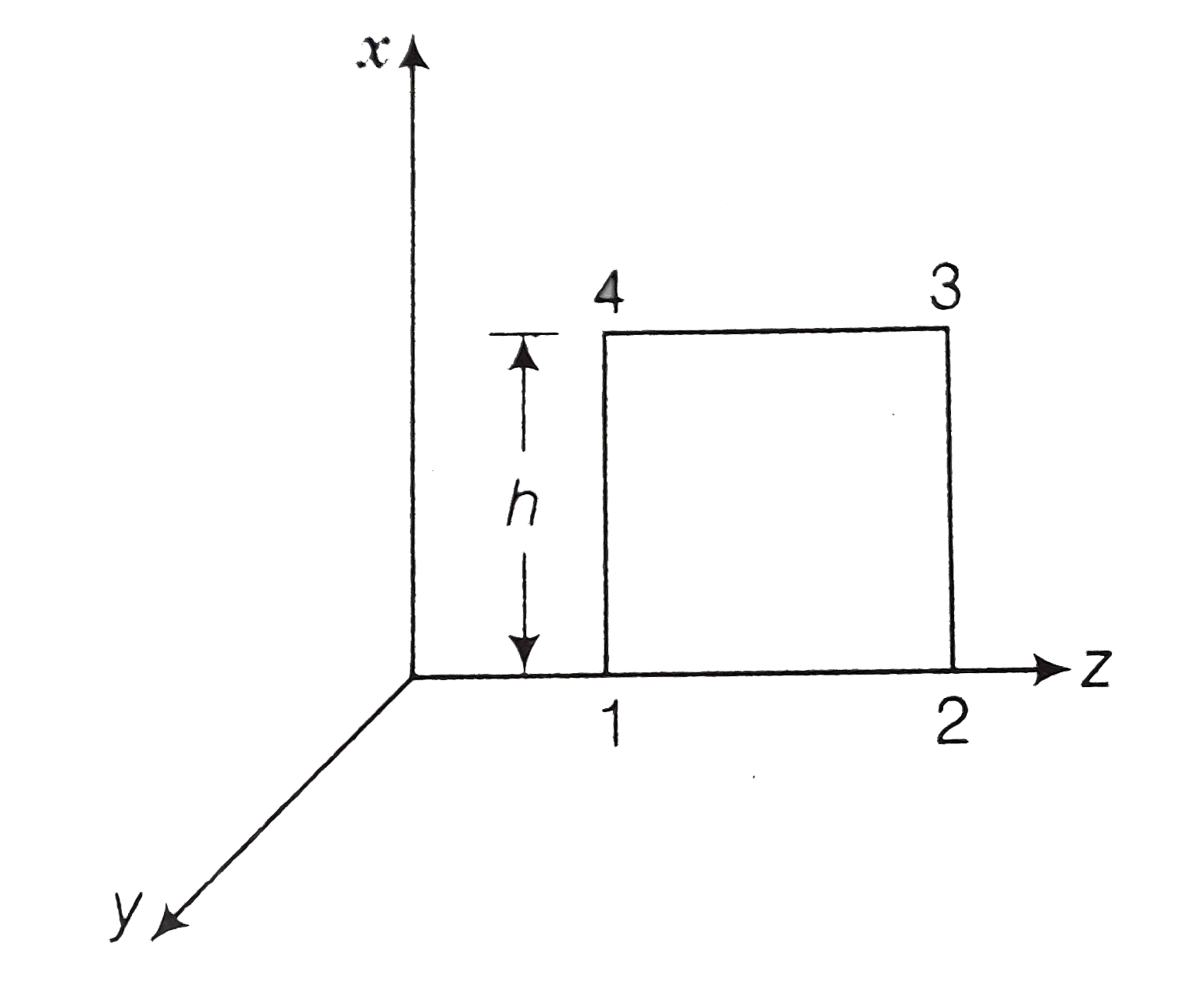
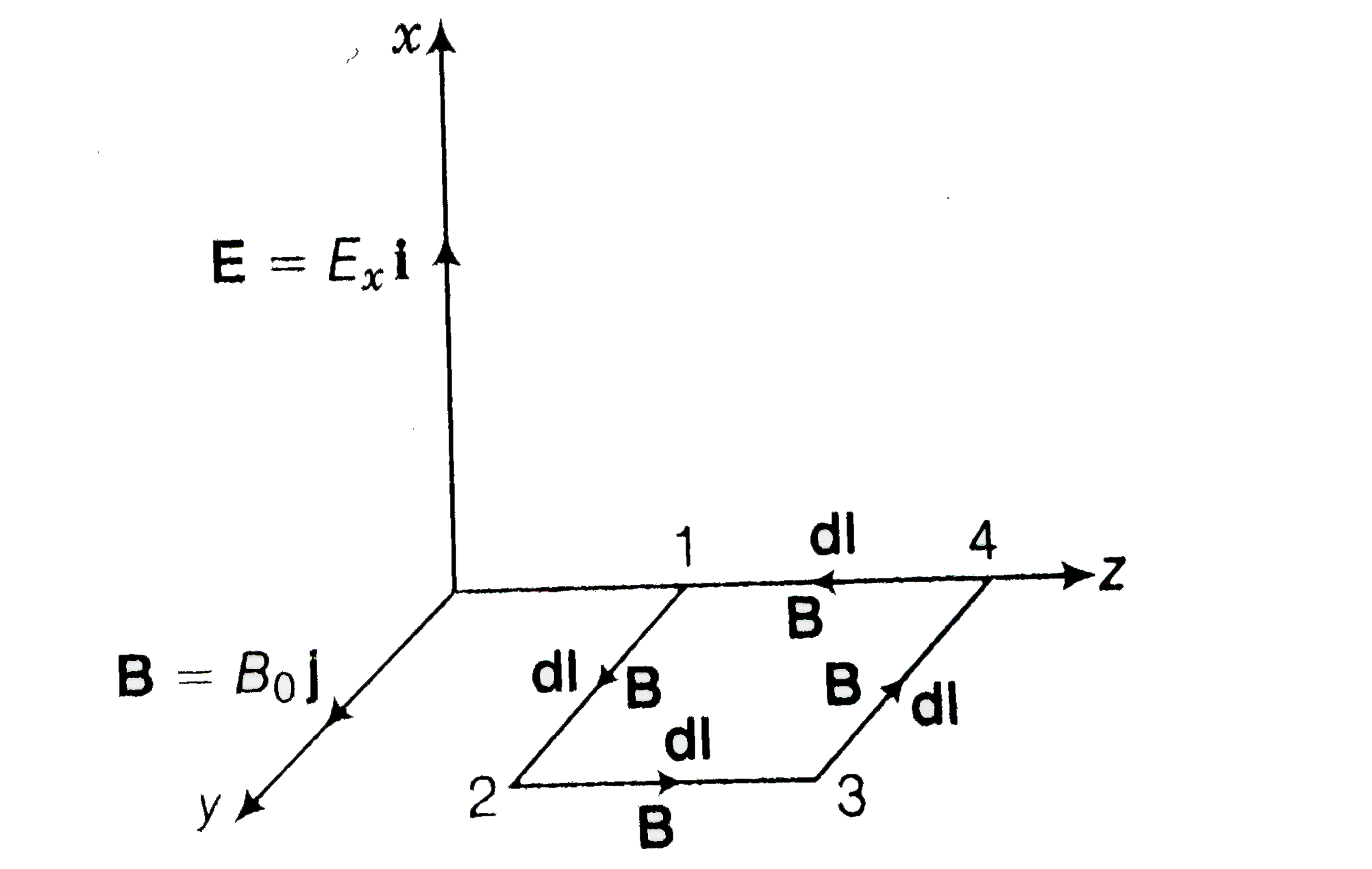(i) consider the figure given below

During the propagation of electromagnetic wave a along z-axis let electric field vector `(E)` be along x-axis and megnetic field vector B along y-axis i.e., `E=E_(0)hati " and " B=B_(0) hatj`
Line intergral of E over the closed rectangular path 1234 in x-z plane of the figure
`ointE.dl =underset(1)overset(2)(int)E.dl +underset(2)overset(3)(int)E.dl+underset(3)overset(4)(int)E.dl+underset(4)overset(1)(int)E.dl`
`=underset(1)overset(2)(int)E.dl"cos"90 +underset(2)overset(3)(int)E.dl"cos"0+underset(3)overset(4)(int)E.dl"cos"90+underset(4)overset(1)(int)E.dl"cos"180^(@)`
`=E_(0)h["sin" (kz_(2) -omegat)-"sin"(kz_(1)-gomegat)]`
(ii) For evaluating `intB.ds,` let us consider the rectangle 1234 to be made of strips of are ds = hdz each.
`int B.ds =intB.ds cos 0 =int B.ds =underset(z_(1))overset(z_(2))(int)B_(0)sin(kz-omegat)hdz`
`=(-B_(0)h)/(k)[cos(kz_(2)-omegat)-cos(kz_(1)-omegat)]`

(iii) Given `oint E.dl=(0dphi_(B))/(dt)=-(d)/(dt)ointB.ds`
Putting the values from Eqs. (i) and (ii) we get
`E_(0) h[sin(kz_(2)-omegat)-sin(kz_(1)-omegat)]`
`=(-d)/(dt)[(B_(y)h)/(k) {cos(kz_(2)-omegat)-cos(kz_(1)-omegat)]`
`=(B_(y)h)/(k) omega[sin(kz_(2)-omegat)-sin(kz_(1)-omegat)]`
`rArr" "E_(0)=(B_(0)omega)/(K) =B_(y)c`
`rArr" "(E_(0))/(B_(0)) =c`
(iv) For evaluating `ointB.dl` let us consider a loop 1234 in y-z plane as shown in figure given below
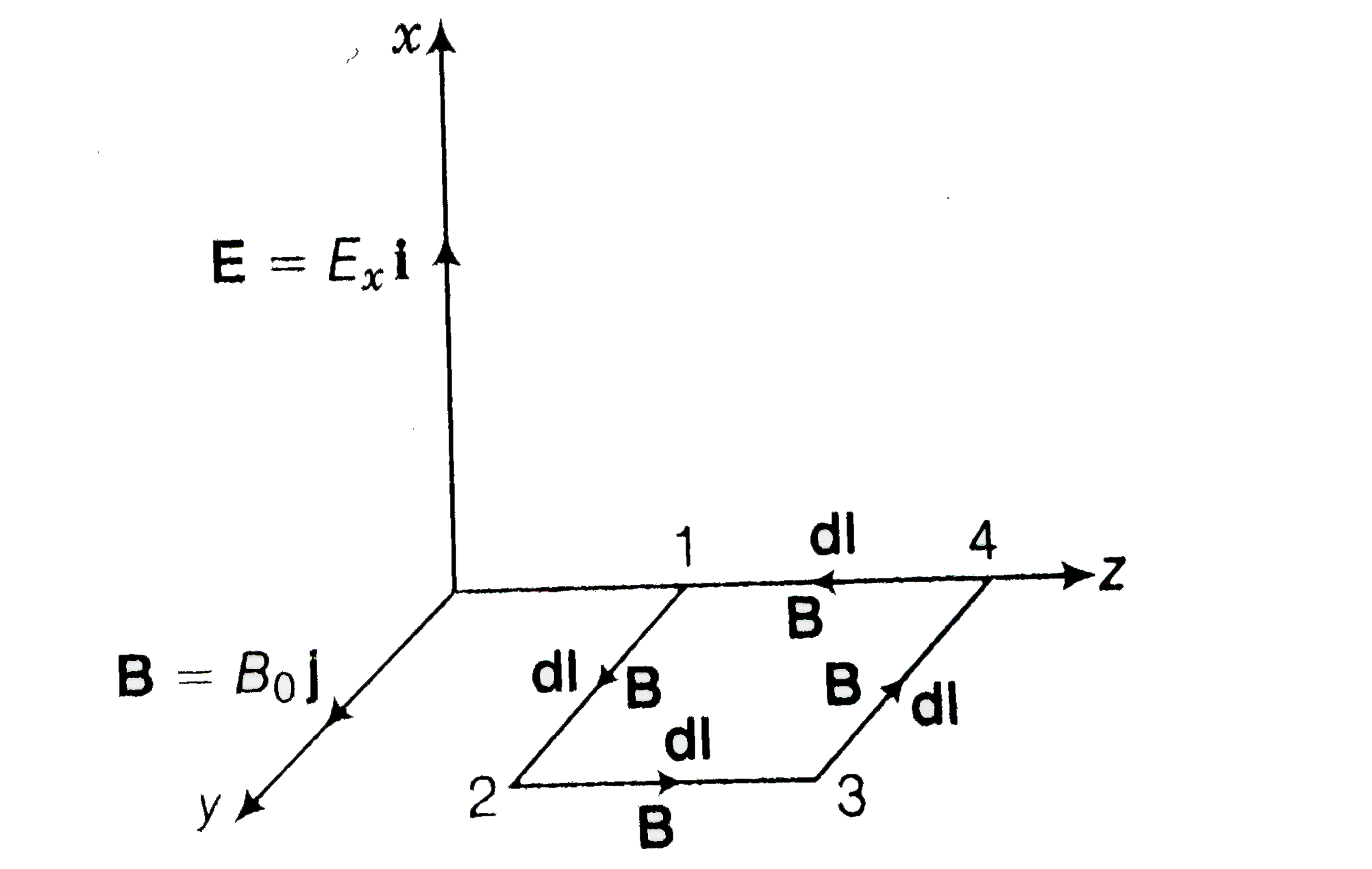
`ointB.dl =underset(1)overset(2)(int)B.dl+underset(2)overset(3)(int)B.dl+underset(3)overset(4)(int)B.dl+underset(4)overset(1)(int)B.dl`
`=underset(1)overset(2)(int)B.dl"cos"0+underset(2)overset(3)(int)B.dlcos90^(@)+underset(3)overset(4)(int)B.dlcos180^(@)+underset(4)overset(1)(int)B.dlcos90^(@)`
`=B_(0)h[sin(kz_(1)-omegat)-sin(kz_(2)-omegat)`
Now to evaluate `phi_(E)=int E.ds` let us consider the rectangle 1234 to be made of strips of area `hd_(2)` each.
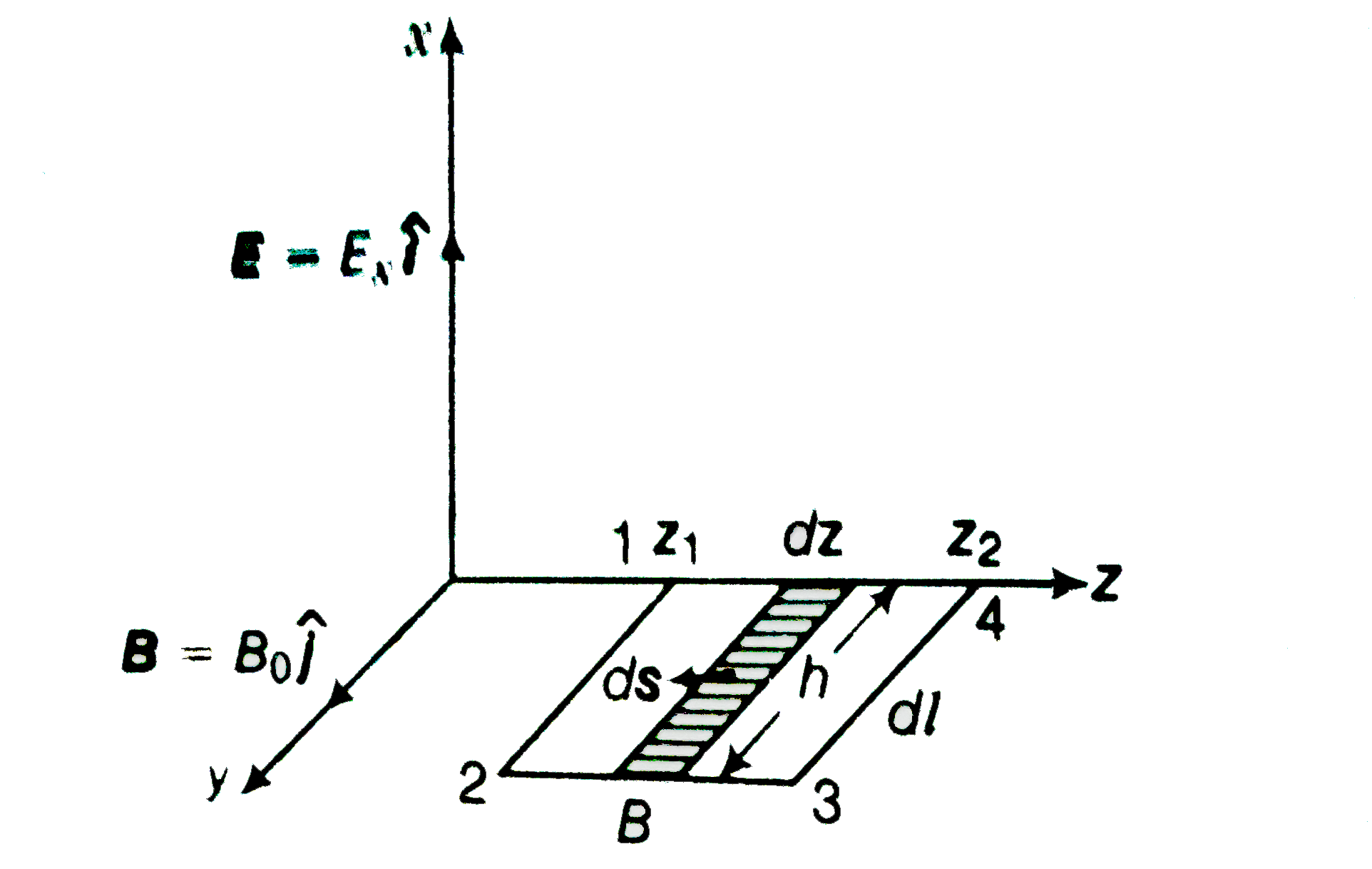
`phi_(E)int E.ds=intEdscos0=intEds =underset(z_(1))overset(z_(2))(int)E_(0)sin(kz_(1)-omegat)hdz`
`=-(E_(0)h)/(K) [cos(kz_(2)-omegat)-cos(kz_(1)-omegat)]`
`:. (dphi_(E))/(dt) =(E_(0)homega)/(K) [sin(kz_(1)-omegat)-sin(kz_(2)-omegat)]`
`ointB.dl =mu_(0) (l+(epsilon_(0)phi_(E))/(dt))I="conduction current"`
`:. oint B.dl =mu_(0) epsilon(dphi_(E))/(dt)`
Using relations obtained in Eqs. (iii) and (iv) and simplifying we get
`B_(0) =E_(0) (omegamu_(0)epsilon_(0))/(K)`
`rArr" "(E_(0))/(B_(0))(omega)/(K) =(1)/(mu_(0)epsilon_(0))`
`"But"" "(E_(0))/(B_(0)) =c " and "omega=ck`
`rArr" "c.c =(1)/(mu_(0)epsilon_(0))"therefore"c=(1)/(sqrt(mu_(0)epsilon_(0))`