Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH-THE HUMAN EYE AND THE COLOURFUL WORLD -LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
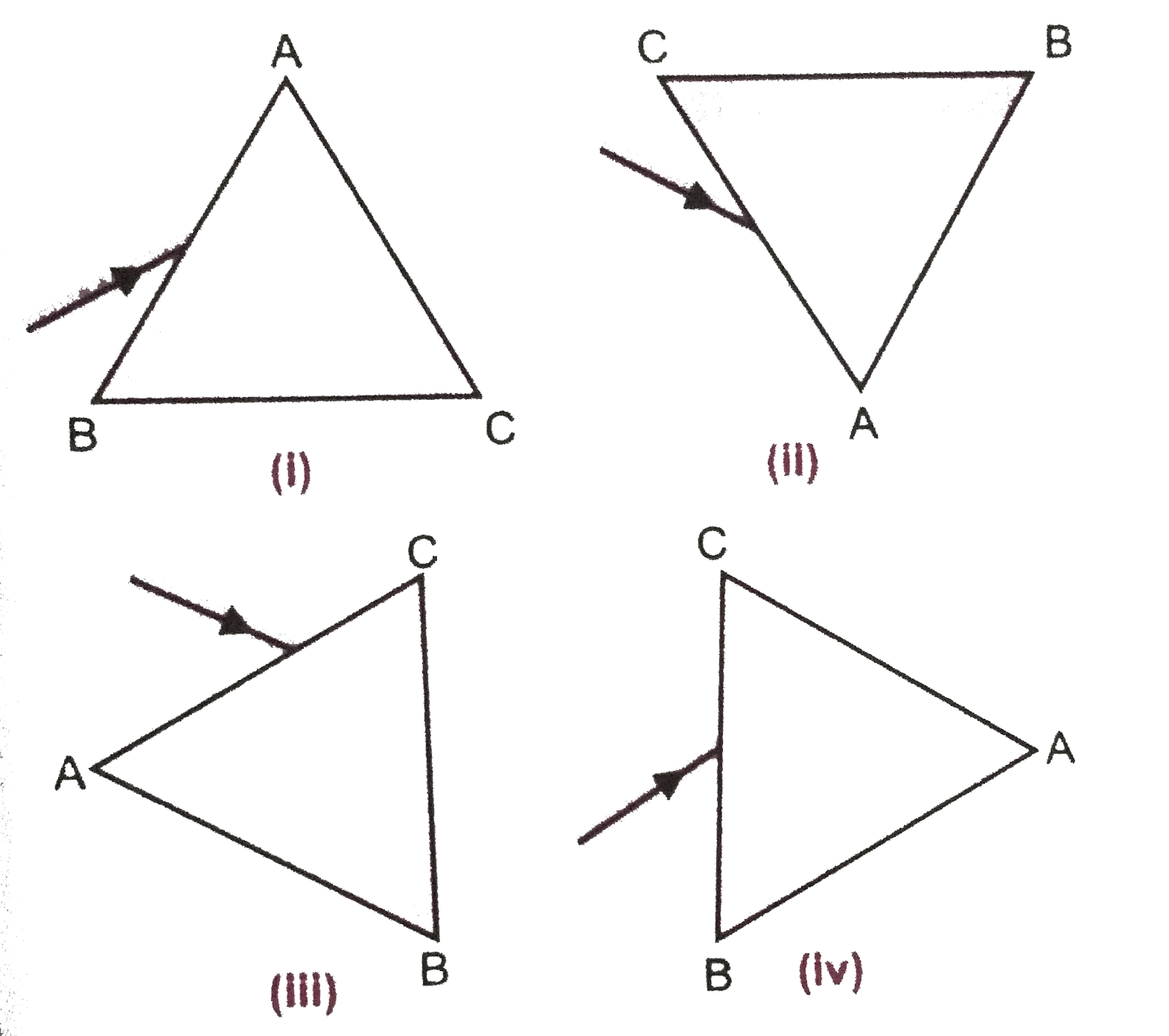
- A prism ABC (with BC as base) is placed in different orientations. A n...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the structure and functioning of human eye. How are we able to...
Text Solution
|
- When do we consider a person to be myopic and hypermetropic? Explain ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the refraction of light through a triangular glass prism using...
Text Solution
|
- How can we explain the reddish appearance of sun at sunrise or sunset?...
Text Solution
|
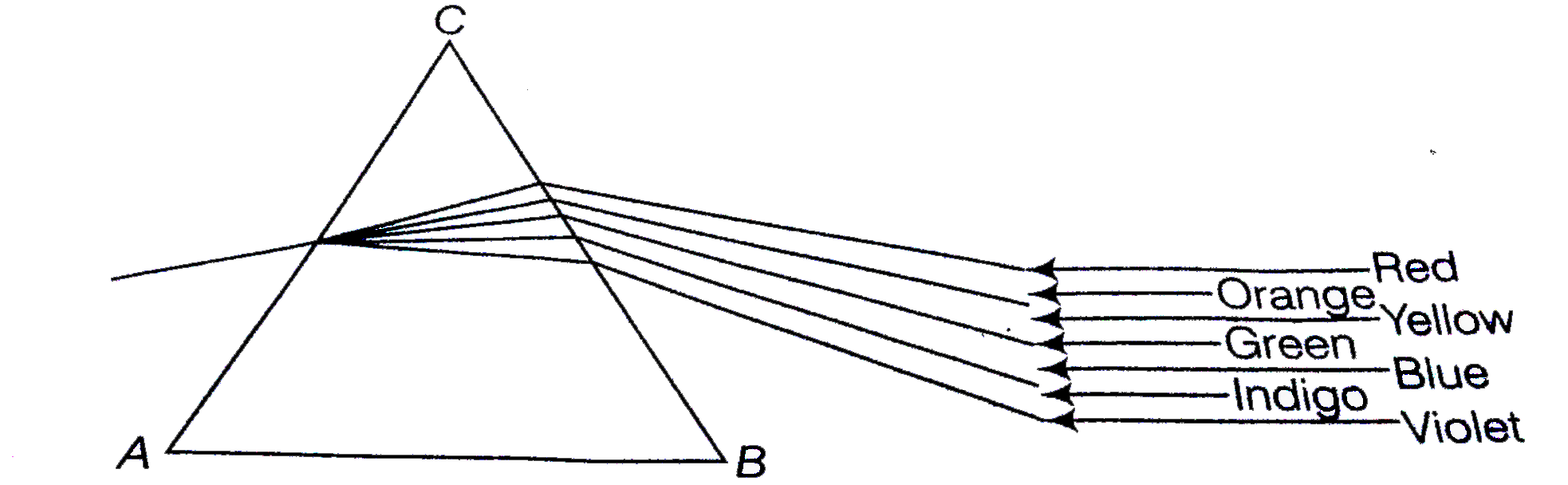
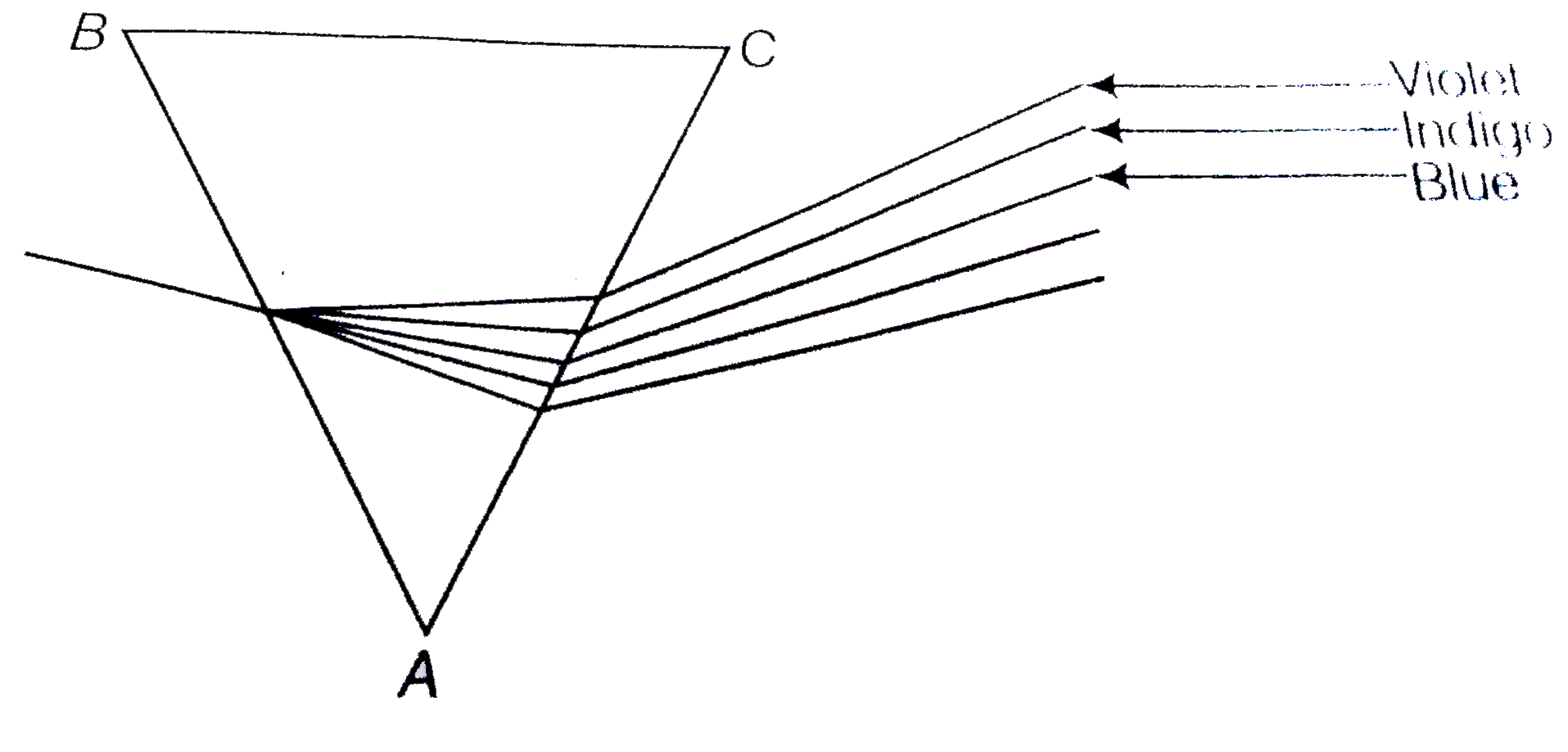
- Explain the phenomenon of dispersion of white light through a glass pr...
Text Solution
|
- How does refraction take place in the atmosphere? Why do stars twinkl...
Text Solution
|
 .
.