Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
HYDROCARBONS
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Matching The Columns|4 VideosHYDROCARBONS
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion and Reason|4 VideosHYDROCARBONS
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Choice Questions (More Than One Options)|9 VideosENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Long Answer Type|5 VideosHYDROGEN
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH-HYDROCARBONS-Short Answer Type Questions
- Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilec addition reaction while...
Text Solution
|
- Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia form trans alkenes....
Text Solution
|
- Rotation around carbon-carbon single bond of ethane is not completely ...
Text Solution
|
- Draw Newman and sawhorse projections for the eclipsed and staggered co...
Text Solution
|
- The intermediate carbocation formed in the reactions of HI,HBr, and HC...
Text Solution
|
- What will be the product obtain as a result of the following reaction?
Text Solution
|
- How will you convert benzene into (a) p-nitrobromobenzene (b) m-nitrob...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following set of compounds in the order of their decreasin...
Text Solution
|
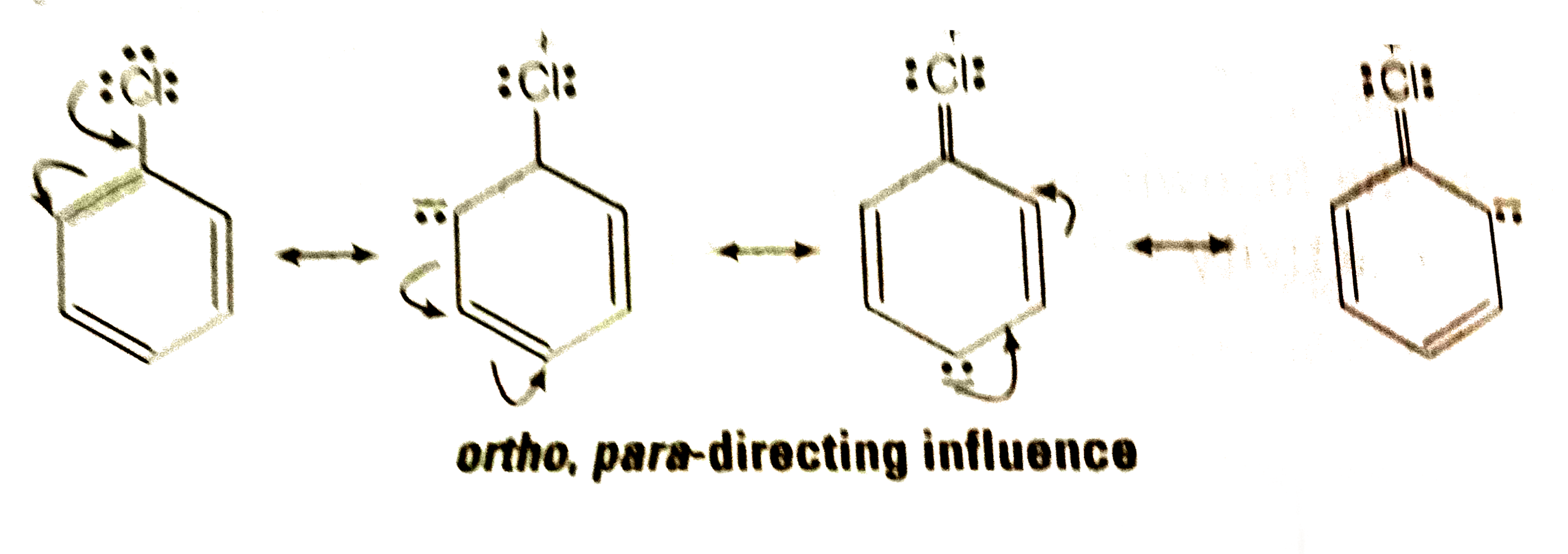
- Despite their-I effect, halogens are o- and p- directing in haloarenes...
Text Solution
|
- Why does presence of a nifro group make the benzene ring less reactive...
Text Solution
|
- Suggest a route for the preparation of nitrobenzene starting from acet...
Text Solution
|
- Predict the major product(S) of the following reactions and explain th...
Text Solution
|
- Nucleophiles and electrophiles are reaction intermediates having elect...
Text Solution
|
- The relative reactivity of 1^(@), 2^(@) and 3^(@) hybrogen's towards c...
Text Solution
|
- Write the structures and names of products obtained in the reactions o...
Text Solution
|
- Write hydrocarbon radicals that can be formed as intermediates during ...
Text Solution
|
- An alkane C(8)H(18) is obtained as the only product on subjectiog a pr...
Text Solution
|
- The ring systems having following characteristics are aromatic. (i) ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds are aromatic according to Huckel's ru...
Text Solution
|
- Suggest a route to prepare ethyl hydrogensulphate (CH(3)-CH(2)-OSO(2)-...
Text Solution
|