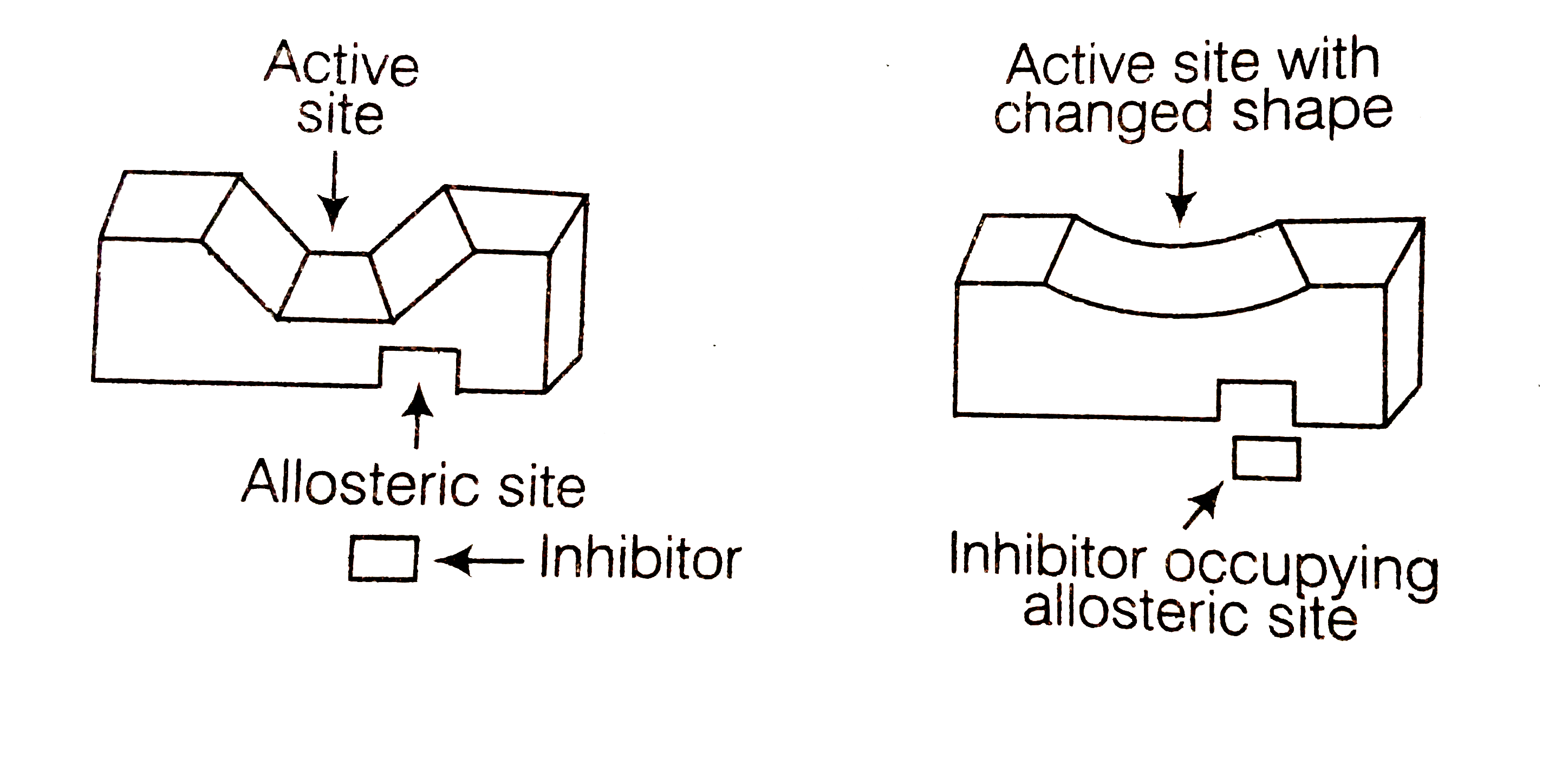Enzymes are responsible to hold the substrates molecule for a chemical reaction and they-provides functional groups which will attack the substrate to carry out the chemical reaction. Drugs which inhibit any of the two activites of enzymes are called enzyme inhibitors.
Enzymes inhibitors can block the binding of the substrate to the active site and hence inhibiting the catalytic acitvity of the enzyme.
Drugs inhibit the attachment of neutral substrate on the active site of enzymes in two different ways as explained below.
(i) Drugs which complete with natural substrate for their attachment on the actvie sites of enzymes are called competitive inhibitors.
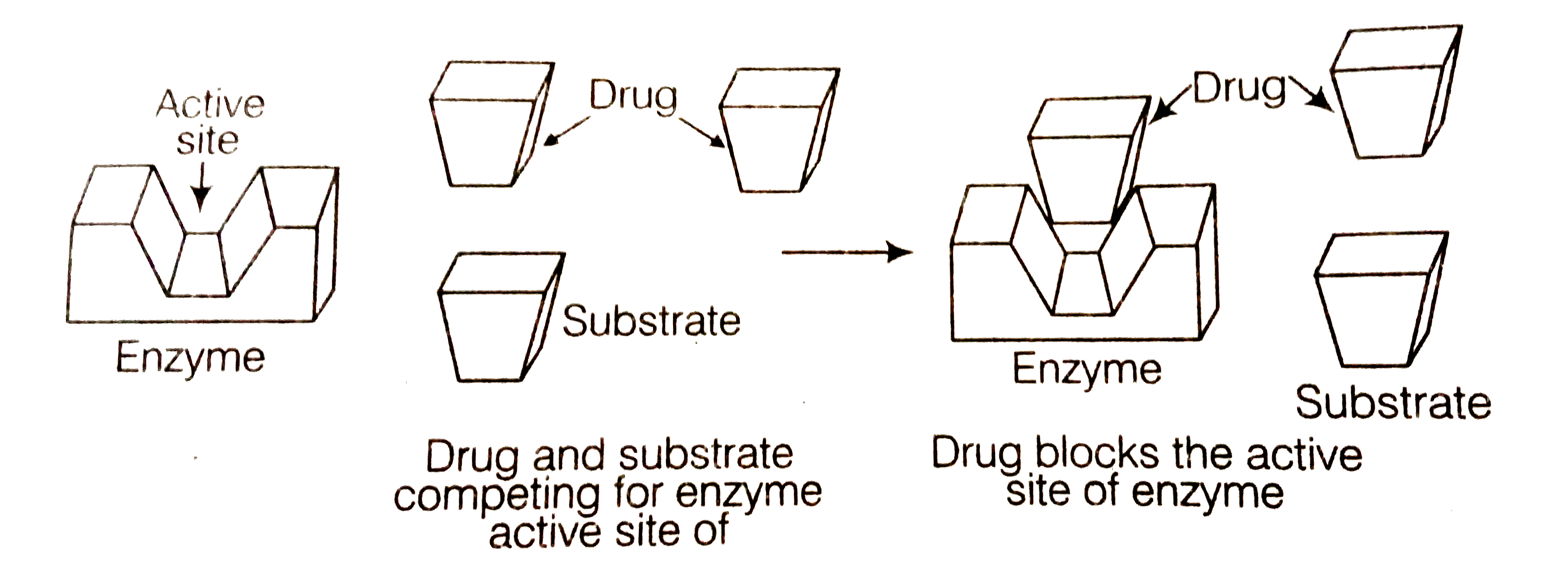
(ii) Some drugs, however, do not bind to the active site but to a different site of the enzyme which is called allosteric site. This binding of the drug at allosteric site changes the shops of the active of the enzymes a way that the natural substrate cannot recognise it. Such enzymes are called non-competitive inhibitors.