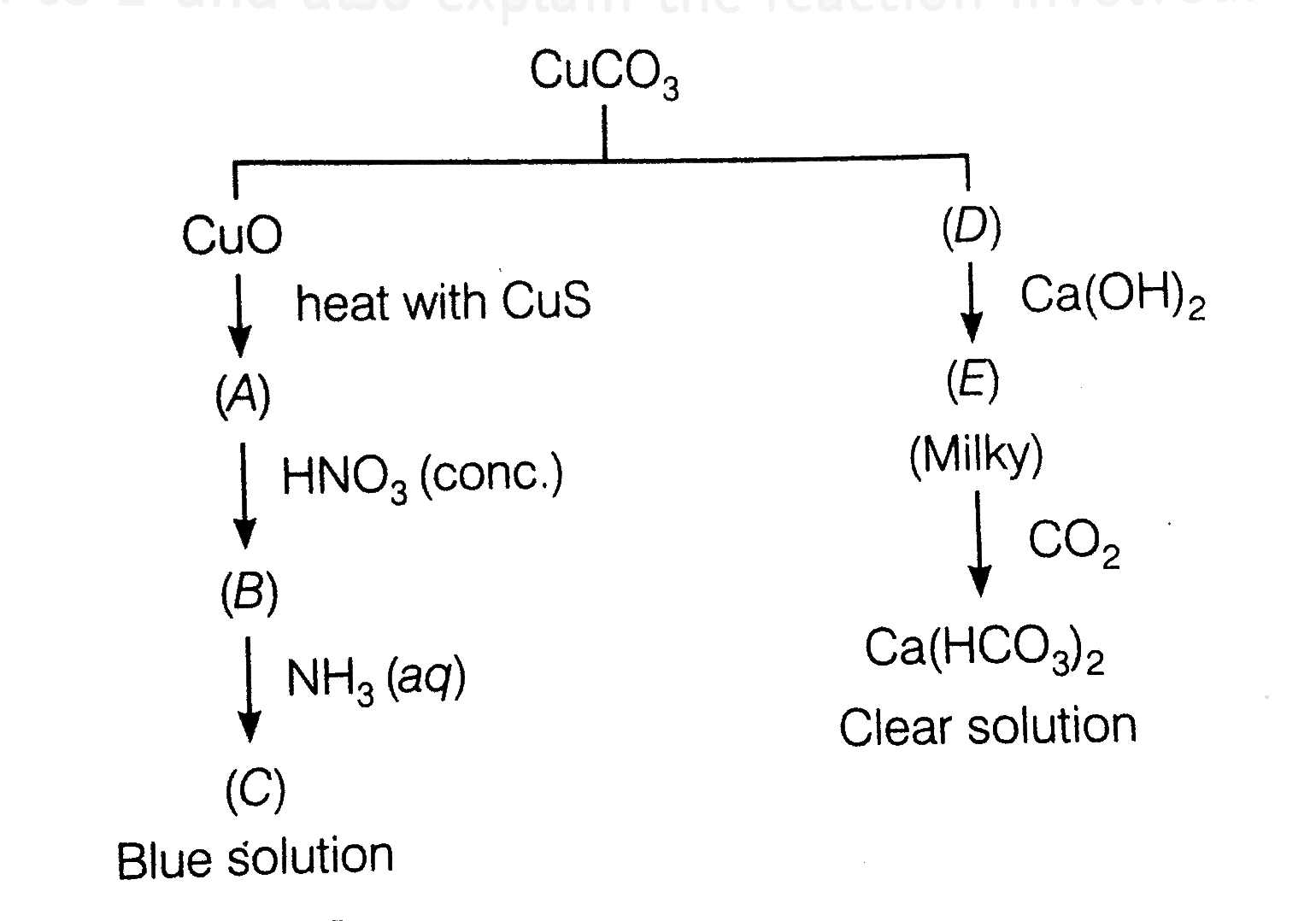Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH-D AND F-BLOCK ELEMENTS-Short Answer Type Question
- Identify A to E and also explain the reaction involved.
Text Solution
|
- Why does copper not replace hydrogen from acids?
Text Solution
|
- Why E^(-) values for Mn, Ni and Zn are more negative than expected?
Text Solution
|
- Why first ionisation enthalpy of Cr is lower than that of Zn?
Text Solution
|
- Transition elements show high melting points. Why?
Text Solution
|
- When Cu^(2+) ion is treated with KI, a white precipitate is formed. Ex...
Text Solution
|
- Out of Cu(2)Cl(2) and CuCl(2), which is more stable and why?
Text Solution
|
- When a brown compound of manganese (A) is treated with HCl it gives a ...
Text Solution
|
- Although fluorine is more electronegative than oxygen, but the ability...
Text Solution
|
- Although Cr^(3+) and Co^(2+) ions have same number of unpaired electro...
Text Solution
|
- Ionisation enthalpies of Ce, Pr and Nd are higher than Th, Pa and U. W...
Text Solution
|
- Although Zr belongs to 4d and Hf belongs to 5d transition series but i...
Text Solution
|
- Cerium shows oxidation state of +4 because
Text Solution
|
- Explain why does colour of KMnO(4) disappear when oxalic acid is added...
Text Solution
|
- When orange solution containing Cr(2)O(7)^(2-) ion is treated with an ...
Text Solution
|
- A solution of KMnO(4) on reduction yields either a colourless solution...
Text Solution
|
- The second and third rows of transition elements resemble each other m...
Text Solution
|
- E^(Theta) of Cu is +0.34V while that of Zn is -0.76 V. Explain.
Text Solution
|
- The halides of transition elements become more covalent with increasin...
Text Solution
|
- While filling up of electrons in the atomic orbitals, the 4s orbital i...
Text Solution
|
- Reactivity of transition elements decreases almost regularly from Sc t...
Text Solution
|