Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH-KINETIC THEORY-Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
- Which of the following diagrams (figure) depicts ideal gas behaviour?
Text Solution
|
- When an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically , its temperature rises ...
Text Solution
|
- Caculate the number of atoms in 39.4 g gold. Molar mass of gold is 197...
Text Solution
|
- The volume of a given mass of a gas at 27^(@)C, 1 atm is 100cc. What w...
Text Solution
|
- The molecules of a given mass of a gas have root mean square speeds of...
Text Solution
|
- Two molecules of a gas have speeds of 9xx10^(6) ms^(-1) and 1xx10^(6) ...
Text Solution
|
- A gas mixture consists of 2.0 moles of oxygen and 4.0 moles of neon a...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the ratio of the mean free paths of the molecules of two gas...
Text Solution
|
- The container shown in figure has two chambers separated by a partitio...
Text Solution
|
- A gas mixture consists of molecules of A,B and C with masses m(A) g...
Text Solution
|
- We have 0.5 g of hydrogen gas in a cubic chamber of size 3 cm kept at ...
Text Solution
|
- When air is pumped into a cycle tyre the volume and pressure of the a...
Text Solution
|
- A balloon has 5.0 mole of helium at 7^(@)C. Calculate (a) the numbe...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the number of degrees of freedom of molecules of hydrogen in...
Text Solution
|
- An insulated container containing monoatomic gas of molar mass m is m...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why (a) there is no atmosphere on moon (b) there is fall i...
Text Solution
|
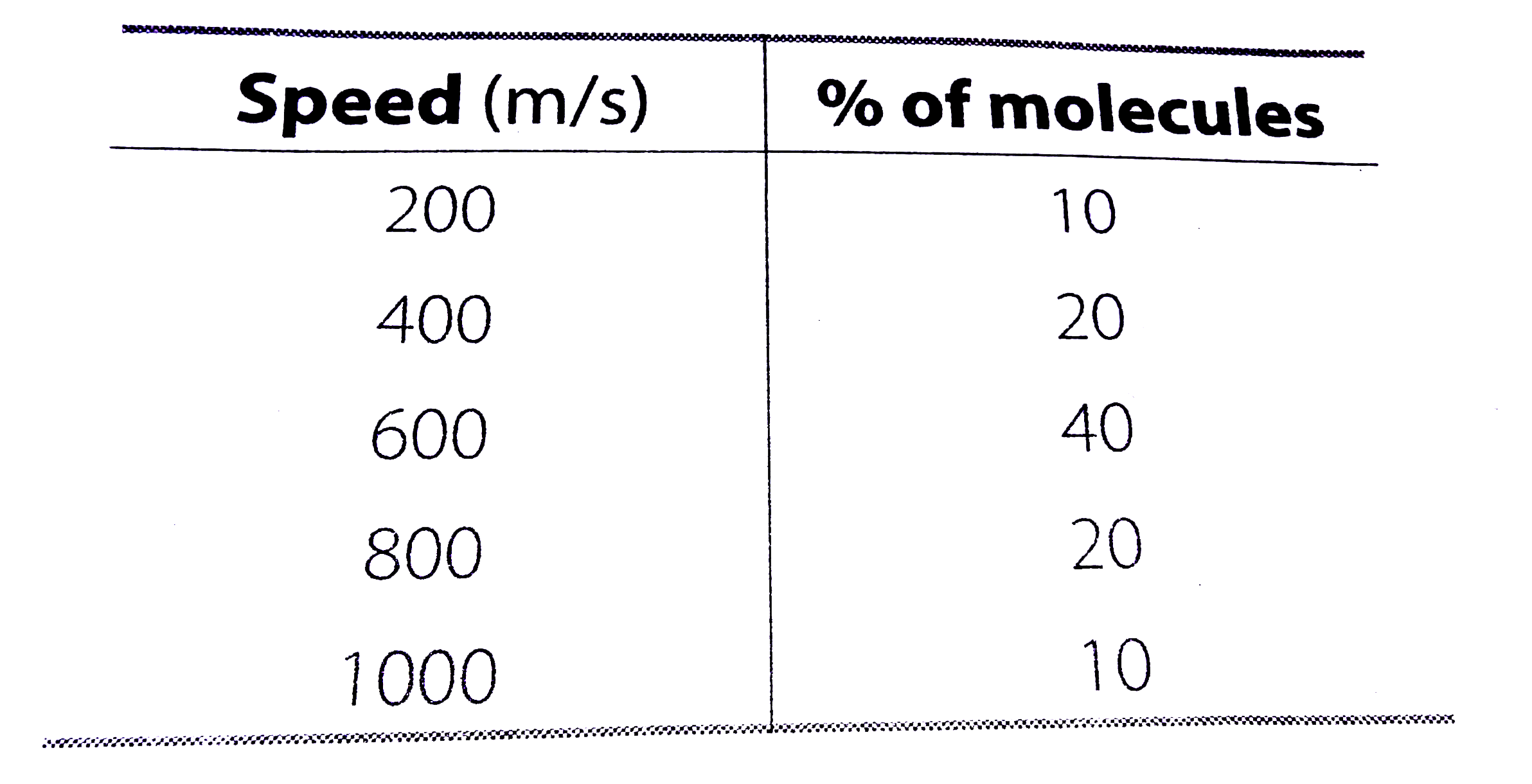
- Consider an ideal gas with following distribution of spedds. (a) C...
Text Solution
|
- Ten small planes are flying at a speed of 150 km//h in total darkness ...
Text Solution
|
- A box of 1.00 m^(3) is filled with nitrogen at 1.50 atm at 300 k. The ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a rectangular block of wood moving with a velocity v(0) in a ...
Text Solution
|