A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELD
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Very short Type Question|6 VideosELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELD
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Short Answer Type question|6 VideosELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELD
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Long Answer Type Question|6 VideosDUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTION|5 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Long|11 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH-ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELD-MCQ s (More than One Options)
- If oint(s) E.ds = 0 Over a surface, then
Text Solution
|
- The Electric field at a point is
Text Solution
|
- If there were only one type of charge in the universe then
Text Solution
|
- Consider a region inside which, there are various types of charges but...
Text Solution
|
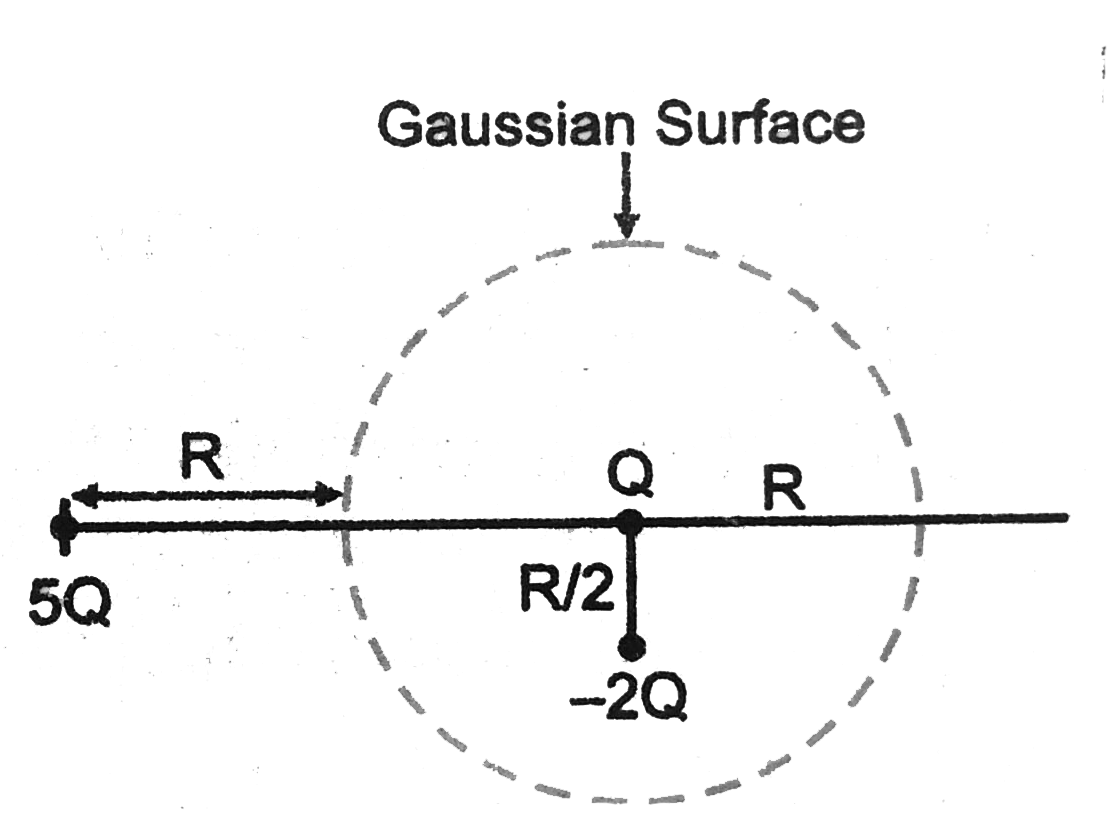
- Refer to the arrangement of charges in Fig and a Gaussian surface of r...
Text Solution
|
- A positive charge Q is uniformly distributed along a circular ring of ...
Text Solution
|