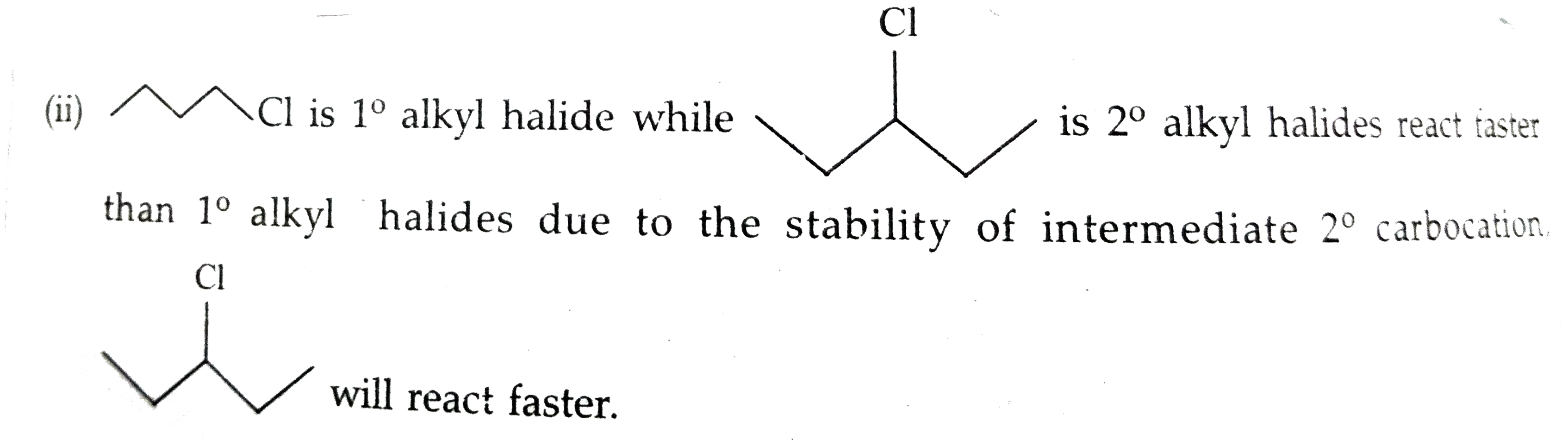
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
XII BOARDS
XII BOARD PREVIOUS YEAR PAPER ENGLISH|Exercise Set I|31 VideosXII BOARDS
XII BOARD PREVIOUS YEAR PAPER ENGLISH|Exercise Set II|10 VideosXII BOARDS
XII BOARD PREVIOUS YEAR PAPER ENGLISH|Exercise Questions|29 VideosSAMPLE PAPER 2019
XII BOARD PREVIOUS YEAR PAPER ENGLISH|Exercise SECTION: D|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
XII BOARD PREVIOUS YEAR PAPER ENGLISH-XII BOARDS-OUTSIDE DELHI (SET-I)
- Answer the following : (i) Which neutral molecule would be isoelectr...
Text Solution
|
- Write complete chemical equation for : (i) Oxidation of Fe^(2+)"by" ...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Why are haloalkanes more reactive towards nucleophilic substitutio...
Text Solution
|
- Complete following reaction equation: (i) C(6)H(5)N(2)Cl+KIrarr........
Text Solution
|
- Write chemical reaction each to illustrate the following : (i) Hofma...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following in an incrasing order of absic strength in water...
Text Solution
|
- (i) What are thermosetting polymers ? Give one example (ii) Give che...
Text Solution
|
- Silver crystallises in a fcc lattice. The edge length of its unit is 4...
Text Solution
|
- A solution containing 8 g of substances in 100 g of diethyl ether boli...
Text Solution
|
- Calcualte the temperature at which a solution containing 54g of glucos...
Text Solution
|
- Explain what is observed when (i) KCl, an electrolyte, is added to ...
Text Solution
|
- What chemcial principal is involved in choosing a reducing agent for g...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the oxidising action of potassium dichromate and write the io...
Text Solution
|
- (a) What is the basis of formation of the spectro-chemical series? (...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Name the reagents and write the chemical equations for the prepar...
Text Solution
|
- What happenes when D-glucose is treated with the following reagents? ...
Text Solution
|
- Mention one use each of the following drugs : (i) Ranitidine (ii...
Text Solution
|
- Define the following : (i) Order of reaction (ii) Activation energ...
Text Solution
|
- The half life for radioactive decay of .^(14)C is 5730 years. An archa...
Text Solution
|
- Assign reasons for the following (i) Sulphur vapour is paramagnetic...
Text Solution
|