Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
XII BOARDS
XII BOARD PREVIOUS YEAR PAPER ENGLISH|Exercise [SET-II]|10 VideosXII BOARDS
XII BOARD PREVIOUS YEAR PAPER ENGLISH|Exercise [SET-III]|10 VideosXII BOARDS
XII BOARD PREVIOUS YEAR PAPER ENGLISH|Exercise Delhi Board : Set - III|7 VideosSAMPLE PAPER 2019
XII BOARD PREVIOUS YEAR PAPER ENGLISH|Exercise SECTION: D|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
XII BOARD PREVIOUS YEAR PAPER ENGLISH-XII BOARDS-[SET-I]
- Complete the following chemical reaction equations : (i) XeF(2)...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following chemical equations : (i) MnO(4)^(-) (aq) + ...
Text Solution
|
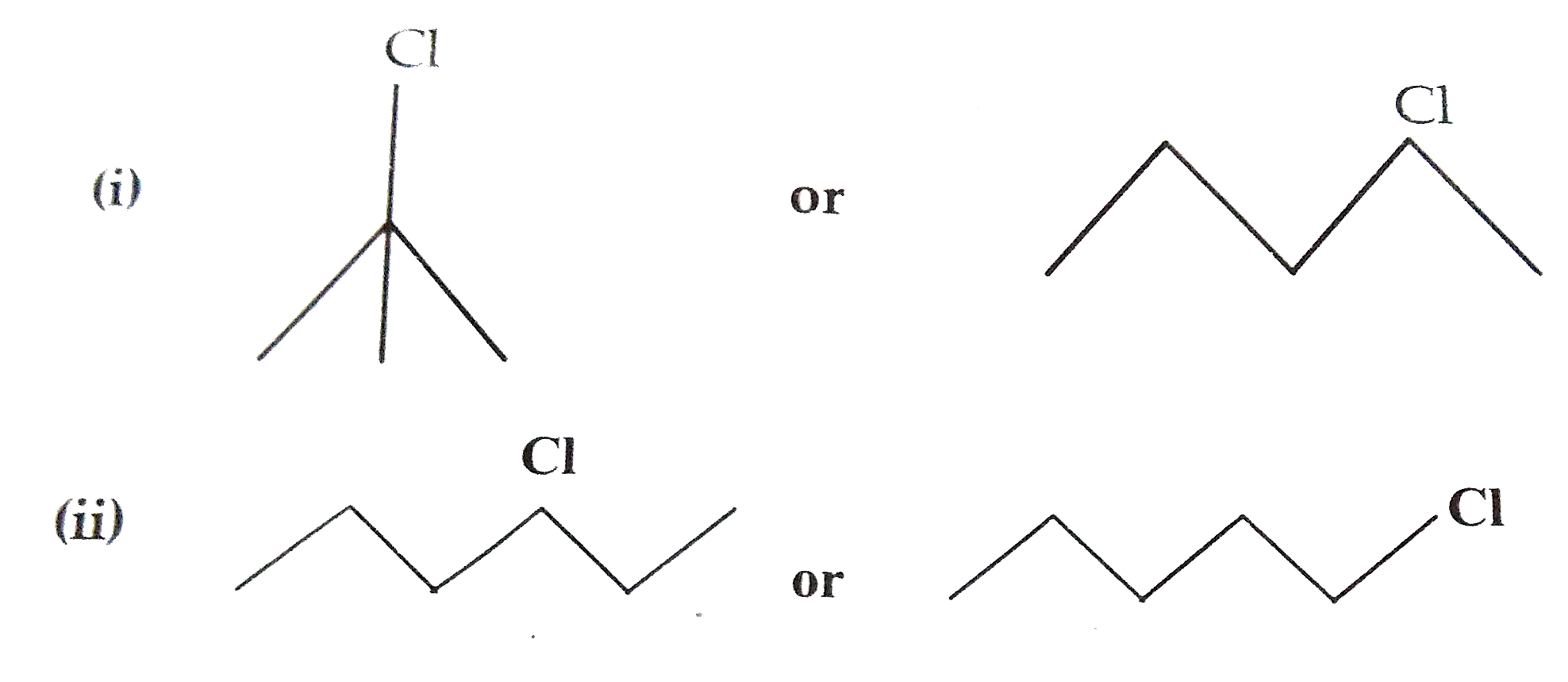
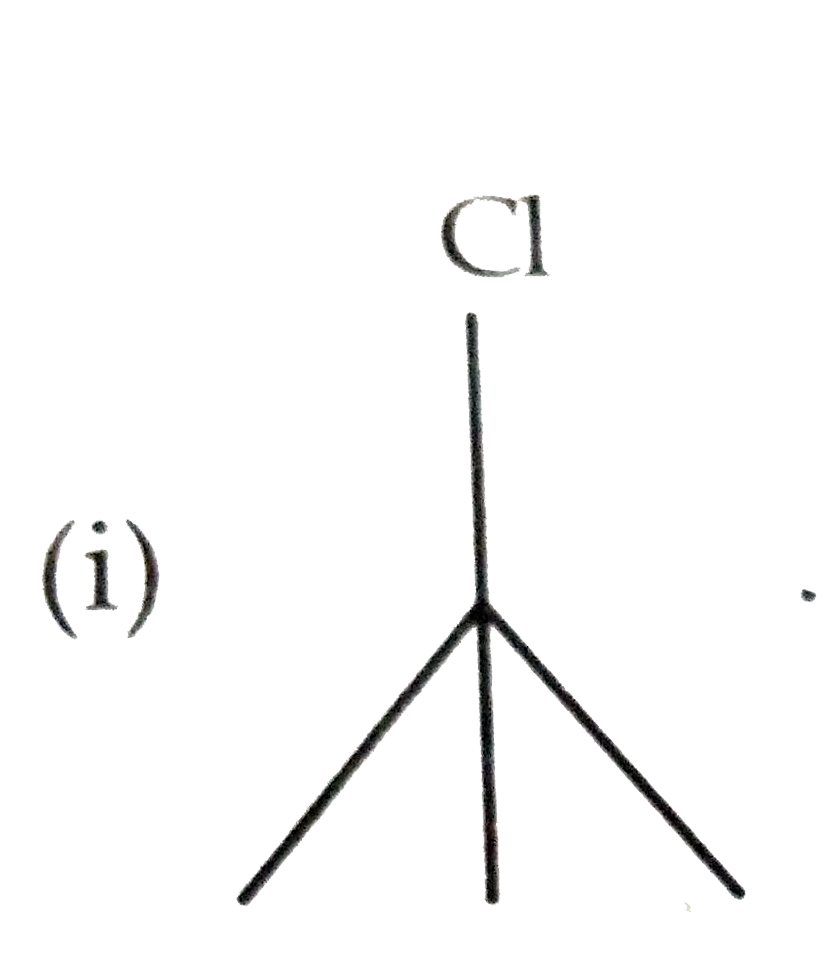
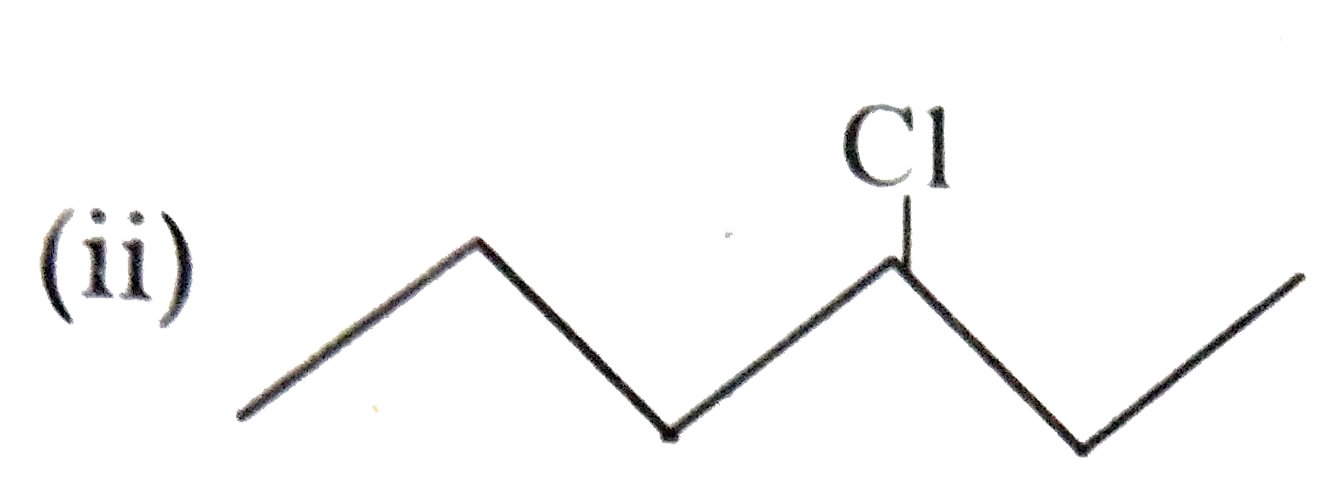
- Which one in the following pairs undergoes S(N)1 substitution reactio...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the follwing reaction equations : (i) (ii) CH(3)CH...
Text Solution
|
- Name the four bases present in DNA. Which one of these is not present ...
Text Solution
|
- Name two fat soluble vitamins, their sources and the diseases caused d...
Text Solution
|
- Differentiate between the molecular structures and behaviour of thermo...
Text Solution
|
- A first order reaction has a rate constant of 0.0051 min^(-1). If we b...
Text Solution
|
- Silver crystallises with face - centred cubic unit cells .each side of...
Text Solution
|
- A copper-silver cell is set up. The copper ion concentration in it is ...
Text Solution
|
- Whate happens in the following activities and why? (i) An electrol...
Text Solution
|
- Give a suitable example for each, explain the following : (i) Crysta...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following complexes with respect to structural shapes of u...
Text Solution
|
- Classify the following as primary ,secondary and tertiary alcohols : ...
Text Solution
|
- How would you account for the following : (i) The metallic radii of ...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following reaction equations: (i) R-overset(O)over...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the following substance with one suitable expample of each t...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Define the following terms: (i) Mole fraction (ii) Van't Hoff fa...
Text Solution
|
- (a) What is meant by: (i) Colligative properties (ii)Molality of a sol...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the structures of the following : (i) H(2)S(2)O(8) (ii...
Text Solution
|
 :
:  :
: