Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
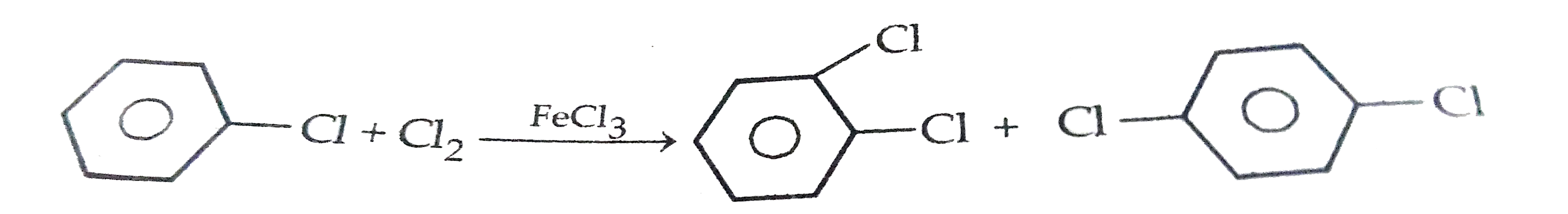
- What happens when (i) chlorobenzene is treated with Cl(2)//FeCl(3) ...
Text Solution
|
- What happens when (i) n-butyl chloride is treated with alcoholic KOH...
Text Solution
|
- What happens when: (i). Ethyl chloride is treated with NaI in the pr...
Text Solution
|
- What happens when: (i). Methyl chloride is treated with alcoholic KC...
Text Solution
|
- What happens when (i) chlorobenzene is treated with Cl(2)//FeCl(3) (ii...
Text Solution
|
- What happens when (i) n-butyl chloride is treated with alcoholic KOH. ...
Text Solution
|
- क्या होता है जब- क्लोरोबेंजीन को Cl(2)//FeCl(3) के साथ उपचारित किया ...
Text Solution
|
- क्या होता है जब- एथिल क्लोराइड को AgNO(2) के साथ उपचारित किया जाता ह...
Text Solution
|
- क्या होता है जब- 2-ब्रोमोपेटेन को ऐल्कोहॉली KOH के साथ उपचारित किया ...
Text Solution
|