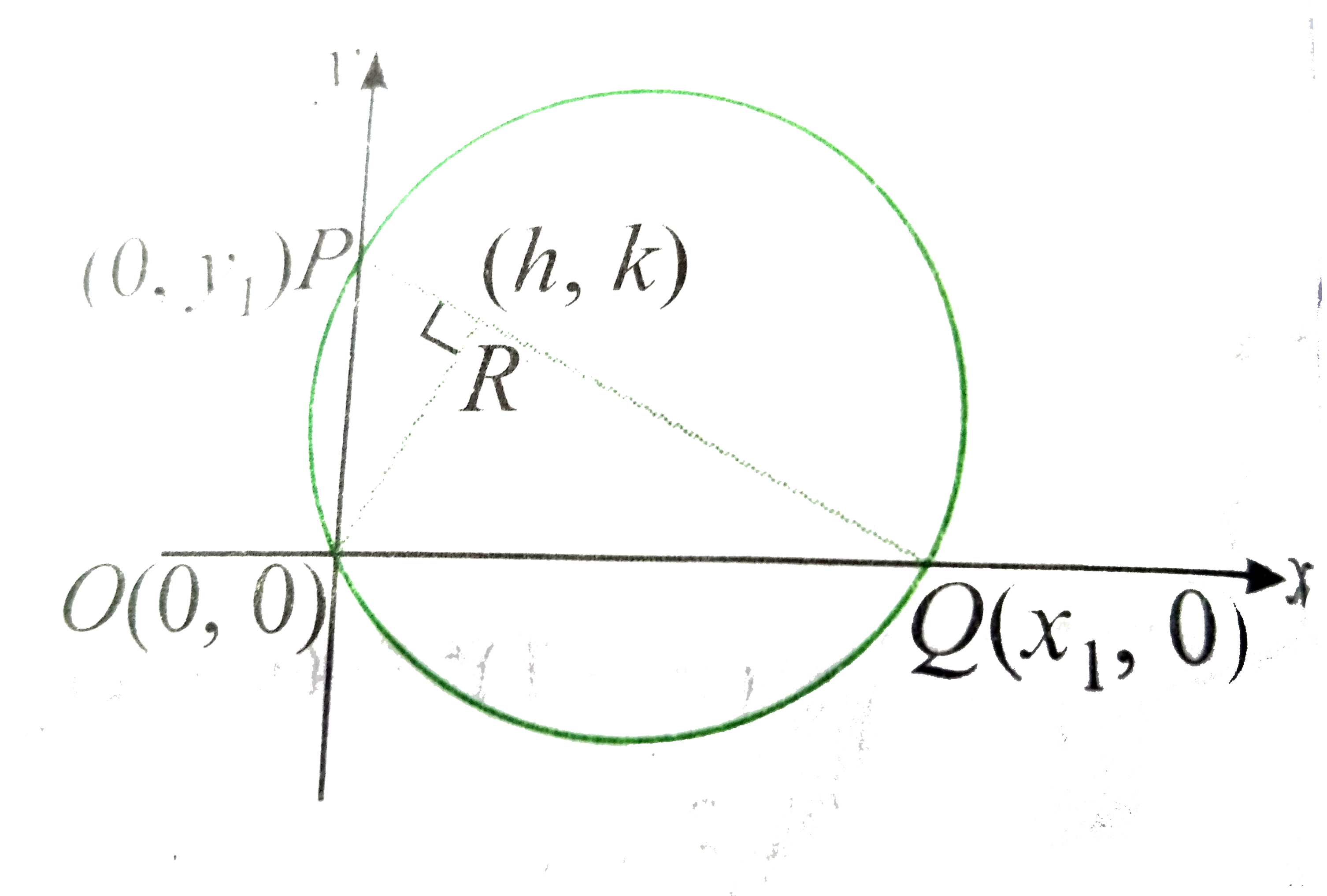A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CIRCLE
CENGAGE ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct Anser Type|29 VideosCIRCLE
CENGAGE ENGLISH|Exercise Linked Comprehension Type (For Problem 1-3)|3 VideosCIRCLE
CENGAGE ENGLISH|Exercise CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE 4.20|1 VideosBINOMIAL THEOREM
CENGAGE ENGLISH|Exercise Matrix|4 VideosCIRCLES
CENGAGE ENGLISH|Exercise Comprehension Type|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE ENGLISH-CIRCLE -Excercises (Single Correct Answer Type)
- about to only mathematics
Text Solution
|
- A B C D is a square of unit area. A circle is tangent to two sides of ...
Text Solution
|
- A circle of constant radius a passes through the origin O and cuts the...
Text Solution
|
- The circle x^2+y^2=4 cuts the line joining the points A(1, 0) and B(3,...
Text Solution
|
- If a circle of radius R passes through the origin O and intersects the...
Text Solution
|
- (6, 0), (0, 6) and (7, 7) are the vertices of a triangle. The circle i...
Text Solution
|
- If O is the origin and O Pa n dO Q are the tangents from the origin to...
Text Solution
|
- about to only mathematics
Text Solution
|
- If the conics whose equations are S-=sin^2thetax^2+2h x y+cos^2thetay^...
Text Solution
|
- From a point R(5, 8) two tangents RP and RQ are drawn to a given circl...
Text Solution
|
- The ends of a quadrant of a circle have the coordinates (1, 3) and (3,...
Text Solution
|
- P is a point on the circle x^2+y^2=9 Q is a point on the line 7x+y+3=0...
Text Solution
|
- Find the equation of the circle which touch the line 2x-y=1 at (1,1) a...
Text Solution
|
- A triangle is inscribed in a circle of radius 1. The distance between ...
Text Solution
|
- The equation of the chord of the circle x^2+y^2-3x-4y-4=0 , which pass...
Text Solution
|
- If O Aa n dO B are equal perpendicular chords of the circles x^2+y^...
Text Solution
|
- A region in the x-y plane is bounded by the curve y=sqrt(25-x^2) and t...
Text Solution
|
- A circle is inscribed into a rhombous ABCD with one angle 60. The dist...
Text Solution
|
- The equation of the line inclined at an angle of pi/4 to the X-a xi s ...
Text Solution
|
- If the y=mx+1, of the circle x^2+y^2=1 subtends an angle of measure 45...
Text Solution
|