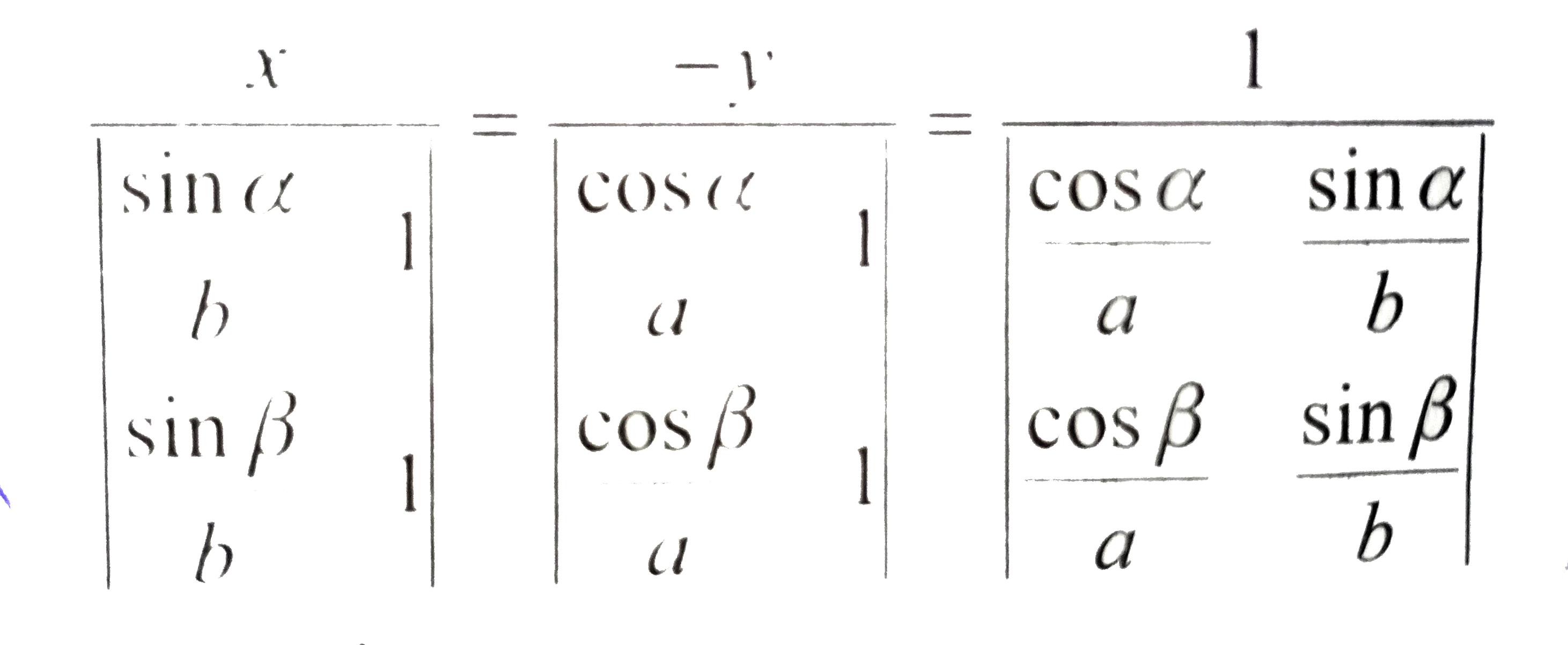
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- If alpha-beta= constant, then the locus of the point of intersection o...
Text Solution
|
- If alpha-beta= constant, then the locus of the point of intersection o...
Text Solution
|
- The locus of the point of intersection of the tangent at the endpoints...
Text Solution
|
- If (x)/(alpha)+(y)/(beta)=1 touches the circle x^(2)+y^(2)=a^(2) then ...
Text Solution
|
- The locus a point P(alpha,beta) moving under the condition that the li...
Text Solution
|
- If a tangent to the parabola y^(2)=4ax intersects the (x^(2))/(a^(2))+...
Text Solution
|
- if a variable tangent of the circle x^(2)+y^(2)=1 intersects the ellip...
Text Solution
|
- The locus of a point P(alpha, beta) moving under the condition that th...
Text Solution
|
- If the eccentric angles of two points P and Q on the ellipse x^2/a^2+y...
Text Solution
|