A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
THEORY OF EQUATIONS
CENGAGE ENGLISH|Exercise MATRIX MATCH TYPE|6 VideosTHEORY OF EQUATIONS
CENGAGE ENGLISH|Exercise NUMERICAL VALUE TYPE|43 VideosTHEORY OF EQUATIONS
CENGAGE ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct Answer Type|38 VideosSTRAIGHT LINES
CENGAGE ENGLISH|Exercise ARCHIVES (NUMERICAL VALUE TYPE)|1 VideosTHREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
CENGAGE ENGLISH|Exercise All Questions|294 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE ENGLISH-THEORY OF EQUATIONS-Linked Comprechension Type
- Let f(x)=x^(2)+bx+c and g(x)=x^(2)+b(1)x+c(1) Let the real roots of ...
Text Solution
|
- Let f(x)=x^(2)+bx+c and g(x)=x^(2)+b(1)x+c(1) Let the real roots of ...
Text Solution
|
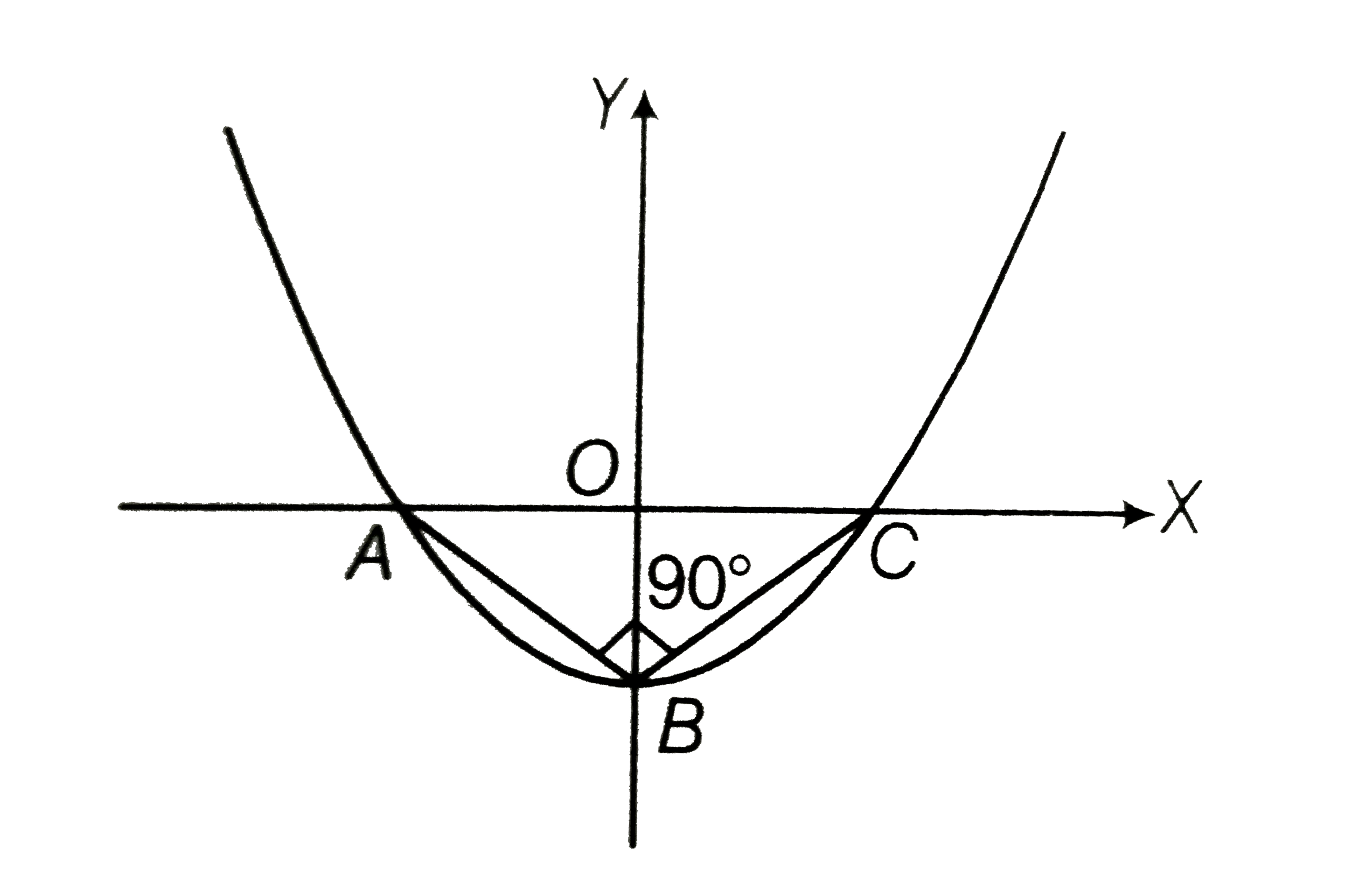
- In the given figue vertices of DeltaABC lie on y=f(x)=ax^(2)+bx+c. The...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figue vertices of DeltaABC lie on y=f(x)=ax^(2)+bx+c. The...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figue vertices of DeltaABC lie on y=f(x)=ax^(2)+bx+c. The...
Text Solution
|
- Let f(x) =4x^2-4ax+a^2-2a+2 be a quadratic polynomial in x,a be any re...
Text Solution
|
- Let f(x) =4x^2-4ax+a^2-2a+2 be a quadratic polynomial in x,a be any re...
Text Solution
|
- Let f(x)= 4x^(2) - 4ax + a^(2) - 2a + 2 such that minimum value fo the...
Text Solution
|
- Consdier the equaiton 2 + |x^(2) + 4x + 3= m , m in R Set of all v...
Text Solution
|
- Consdier the equaiton 2 + |x^(2) + 4x + 3| = m , m in R Set of all...
Text Solution
|
- Consdier the equaiton 2 + |x^(2) + 4x + 3|= m , m in R Set of all v...
Text Solution
|
- If ax^(2)+bx+c=0 have two distinct roots lying int eh interval (0,1),a...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the quadrationax^(2) - bx + c =0,a,b,c in N which has two di...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the quadrationax^(2) - bx + c =0,a,b,c in N which has two di...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the inequation x^(2) + x + a - 9 < 0 The values of the re...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the inequation x^(2) + x + a - 9 lt 0 The values of the re...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the inequation x^(2) + x + a - 9 lt 0 The value of the pa...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the inequation 9^(x) -a3^(x) - a+ 3 le 0, where a is real p...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the inequality 9^(x)-a*3^(x)-a+3le0, where a is a real parame...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the inequality 9^(x)-a*3^(x)-a+3le0, where a is a real parame...
Text Solution
|