Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
MAGNETIC FIELD
HC VERMA ENGLISH|Exercise QUESTIONS FOR SHORT ASNWER|10 VideosMAGNETIC FIELD
HC VERMA ENGLISH|Exercise objective2|9 VideosMAGNETIC FIELD
HC VERMA ENGLISH|Exercise objective 1|10 VideosLIGHT WAVES
HC VERMA ENGLISH|Exercise Question for short Answer|11 VideosMAGNETIC FIELD DUE TO CURRENT
HC VERMA ENGLISH|Exercise questions for short answer|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HC VERMA ENGLISH-MAGNETIC FIELD-Exercises
- A ring of radius 0.1m is made out of thin metallic wire of area of cro...
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic field existing in a region is given by vecB =B0(1+(x)/(l)...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting wire of length l, lying normal to a magnetic field B, mo...
Text Solution
|
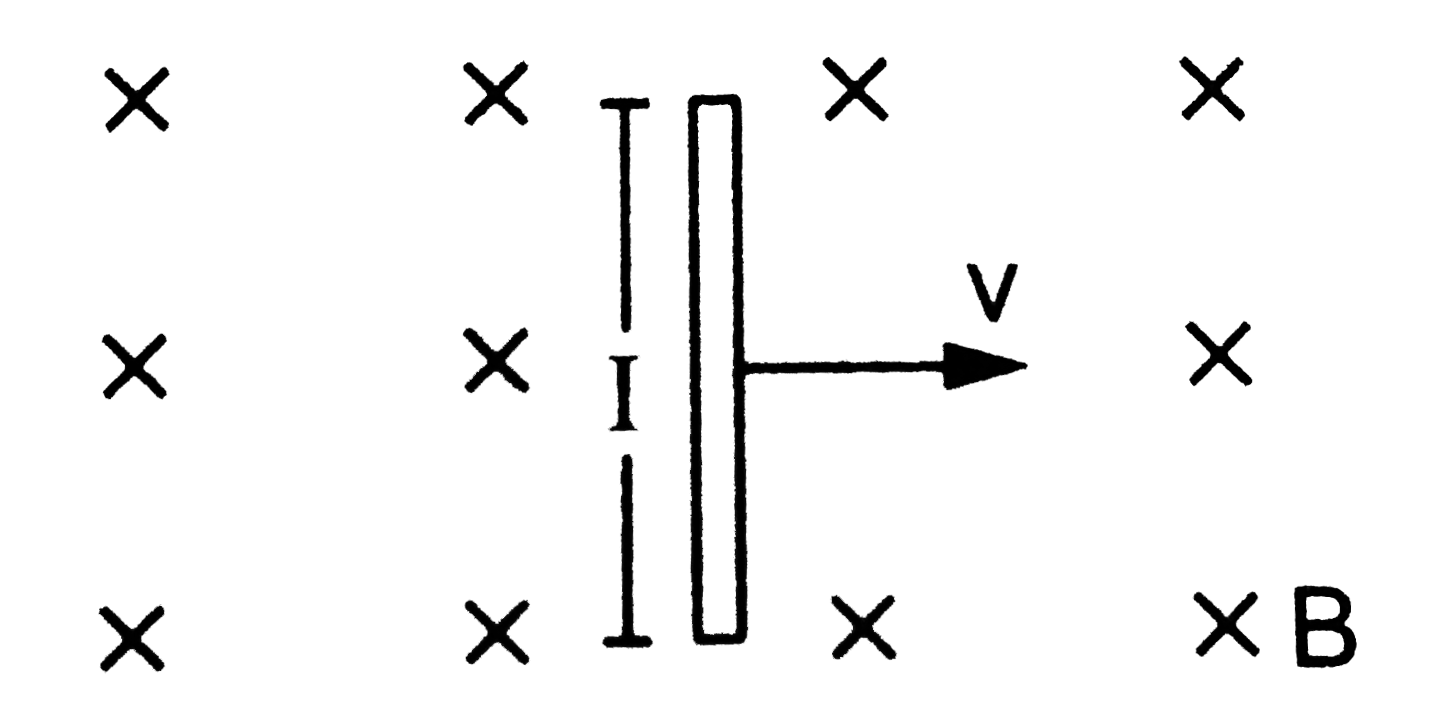
- A currrent I is passed through a silver strip of width d and area of...
Text Solution
|
- A particle having a charge of 2.0X10^(-8) C and a mass of 2.0X10^(-10...
Text Solution
|
- A proton describes a circle of radius 1 cm in a magnetic field of stre...
Text Solution
|
- An electron having a kinetic energy of 100eV circulates in a path of r...
Text Solution
|
- Protons having kinetic energy K emerge from an accelerator as a narrow...
Text Solution
|
- A charged particle is accelerated thrught a potential difference of 12...
Text Solution
|
- Doubly ionized helium ions are projected with a speed of 10kms^(-1) in...
Text Solution
|
- A proton is projected with a velocity of 3X10^6 m s ^(-1) perpendicula...
Text Solution
|
- (a) An electron moves along a circle of radius 1m in a perpendicular m...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m and positive charge q, moving with a uniform velo...
Text Solution
|
- A charged particle (q, m) enters perpendicular in a uniform magnetic f...
Text Solution
|
- A narrow beam of singley charged carbon ions, moving at a constant ve...
Text Solution
|
- Fe^+ ions are accelerated through a potential difference of 500 V and ...
Text Solution
|
- A narrow beam of singly charged potassium ions of kinetic energy 32ke...
Text Solution
|
- Shows a convex lens of focal length 12 cm lying in a uniform magnetic...
Text Solution
|
- Electrons emitted with negligible speed from an electron gun are accel...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles, each having a mass m are placed at a separation d in a ...
Text Solution
|