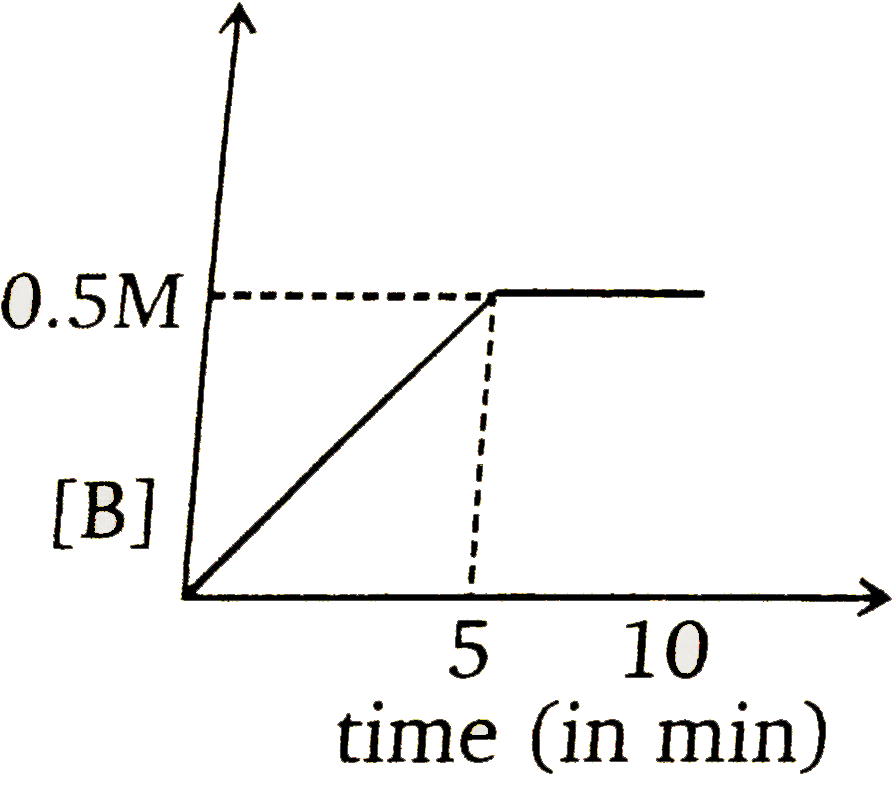
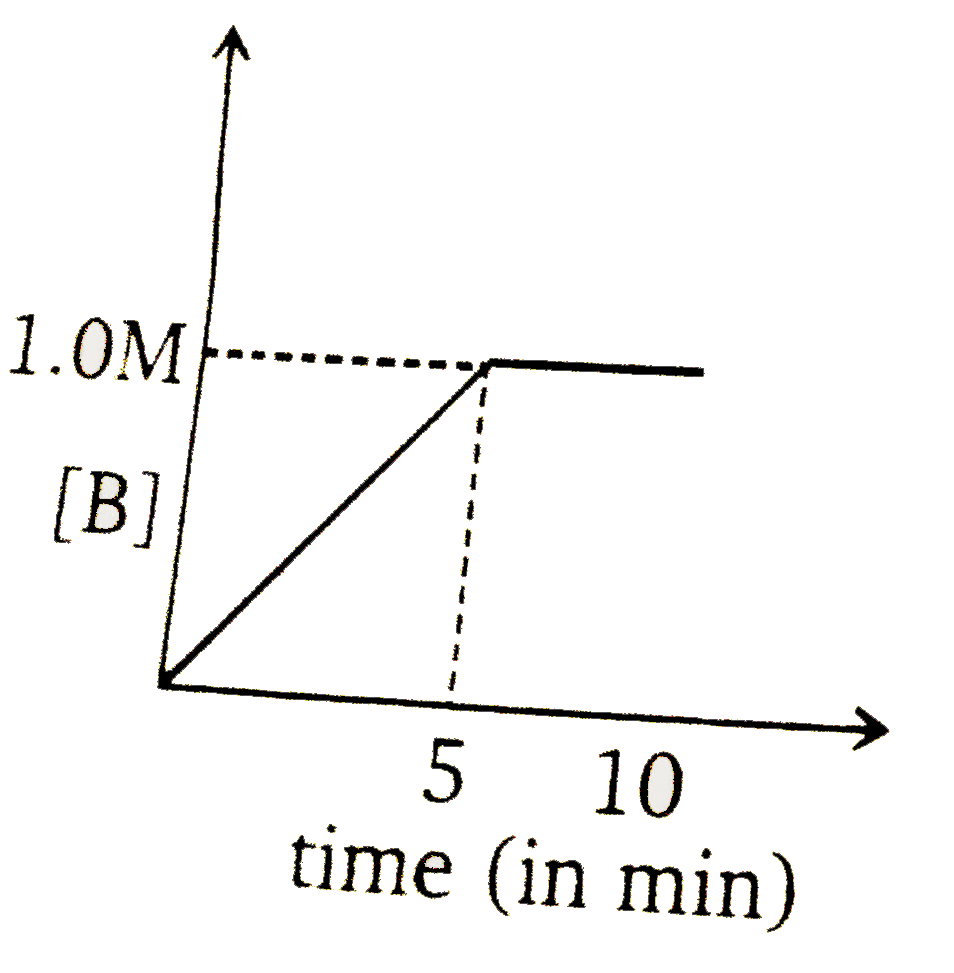
To solve the problem, we need to analyze the given reaction and the information provided. The reaction is:
\[ A(g) \overset{k=0.1 \, \text{M min}^{-1}}{\rightarrow} 2B(g) \]
### Step 1: Determine the Order of the Reaction
The rate constant \( k \) is given as \( 0.1 \, \text{M min}^{-1} \). The units of \( k \) can help us determine the order of the reaction. The general unit of \( k \) is given by:
\[
\text{Units of } k = \text{M}^{1-n} \cdot \text{s}^{-1}
\]
Here, since the unit of \( k \) is \( \text{M min}^{-1} \), we can express it in terms of seconds:
\[
\text{M min}^{-1} = \text{M} \cdot \text{min}^{-1} = \text{M} \cdot \left(\frac{1}{60} \text{s}\right)^{-1} = \text{M} \cdot \text{s}^{-1}
\]
From the unit \( \text{M min}^{-1} \), we can deduce that:
\[
1 - n = 1 \implies n = 0
\]
Thus, the reaction is a **zero-order reaction**.
### Step 2: Write the Rate Law for Zero-Order Reaction
For a zero-order reaction, the rate of reaction is constant and can be expressed as:
\[
\text{Rate} = k = 0.1 \, \text{M min}^{-1}
\]
### Step 3: Calculate the Change in Concentration Over Time
For a zero-order reaction, the change in concentration of \( A \) over time can be described by the equation:
\[
[A] = [A_0] - kt
\]
Where:
- \([A_0]\) is the initial concentration of \( A \) (0.5 M),
- \( k \) is the rate constant (0.1 M/min),
- \( t \) is the time in minutes.
### Step 4: Calculate Concentration of A at \( t = 5 \) minutes
Substituting the known values into the equation:
\[
[A] = 0.5 \, \text{M} - (0.1 \, \text{M min}^{-1})(5 \, \text{min})
\]
\[
[A] = 0.5 \, \text{M} - 0.5 \, \text{M} = 0 \, \text{M}
\]
This means that at \( t = 5 \) minutes, all of \( A \) has reacted.
### Step 5: Calculate Concentration of B
Since the stoichiometry of the reaction shows that 1 mole of \( A \) produces 2 moles of \( B \):
\[
\text{If } A \text{ is completely consumed, then } [B] = 2 \times \text{moles of } A \text{ reacted}
\]
At \( t = 5 \) minutes, \( 0.5 \, \text{M} \) of \( A \) has reacted, thus:
\[
[B] = 2 \times 0.5 \, \text{M} = 1 \, \text{M}
\]
### Step 6: Determine the Graph
At \( t = 5 \) minutes, the concentration of \( B \) is \( 1 \, \text{M} \) and \( A \) is \( 0 \, \text{M} \). Therefore, we need to select the graph that shows \( [B] = 1 \, \text{M} \) at \( t = 5 \) minutes and indicates that the reaction has stopped (i.e., no further increase in \( B \)) after this point.
### Conclusion
The correct graph is the one that shows:
- At \( t = 5 \) minutes, \( [B] = 1 \, \text{M} \)
- No further increase in \( [B] \) after \( t = 5 \) minutes.