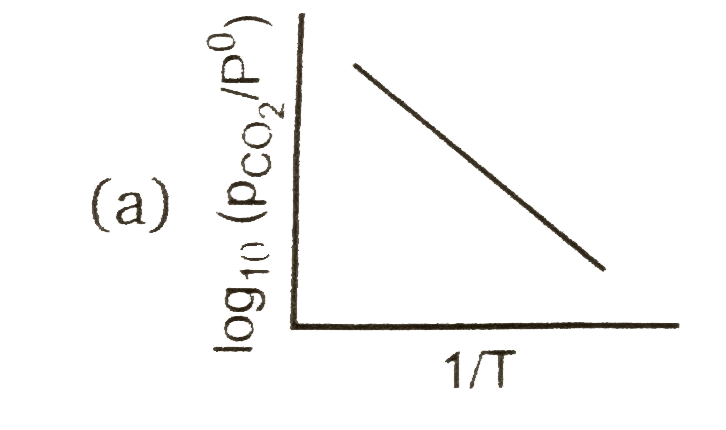
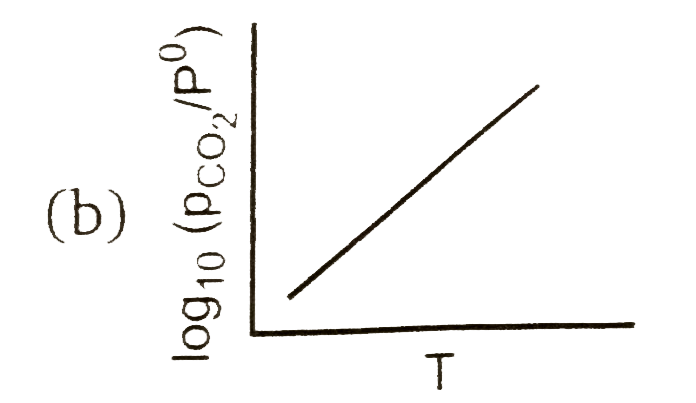
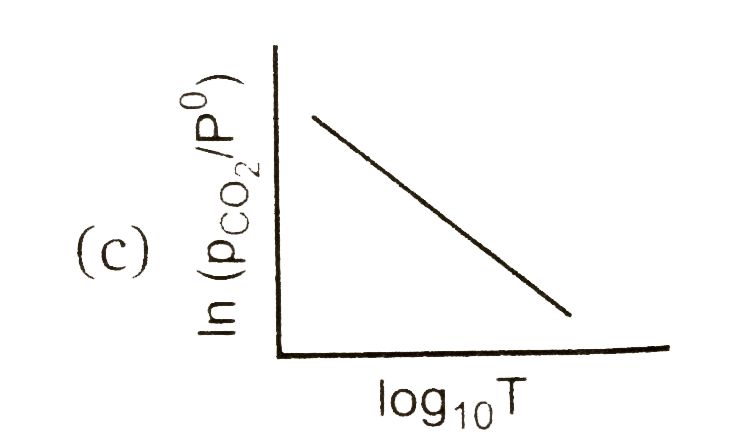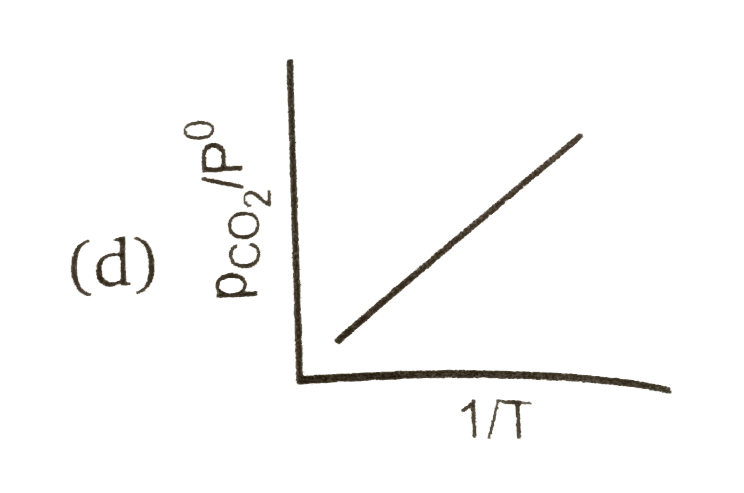A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- For the chemical equilibrium, CaCO(3)(s) hArr CaO(s)+CO(2)(g) Delt...
Text Solution
|
- For the chemical equilibrium, CaCO(3)(s) hArr CaO(s)+CO(2)(g) Delta(r)...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the pressure of CO(2) gas at 700 K in the heterogenous equil...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the reaction CaCO(3)(s) hArr CaO(s) +CO(2)(g) in closed c...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the pressure of CO(2) gas at 700 K in the hetrogeneous equil...
Text Solution
|
- CaCO(3)(s) hArr CaO(s)+CO(2)(g) in closed container at equilibrium. Wh...
Text Solution
|
- which is correct about the following reaction ? CaCO(3)(s) hArr CaO...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction : CaCO(3) (s) hArr CaO (s) + CO(2) (g)
Text Solution
|
- For the chemical equlibrium, CaCo(3(s))hArrCaO(s)+CO(2)(g),DeltaH(r)^(...
Text Solution
|