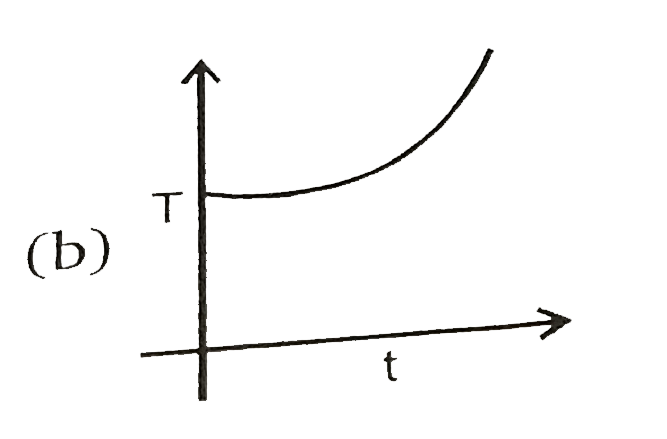
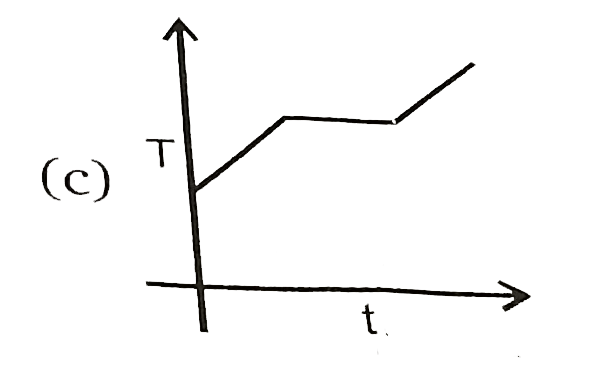
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARENDRA AWASTHI ENGLISH-THERMODYNAMICS-Level 3
- If liquefied oxygen at 1 atmospheric pressure is heated from 50K to 30...
Text Solution
|
- The first law of thermodynamics for a closed system is dU = dq + dw, w...
Text Solution
|
- The first law of thermodynamics for a closed system is dU = dq + dw, w...
Text Solution
|
- If the boundary of system moves by an infinitesimal amount, the work i...
Text Solution
|
- If the boundary of system moves by an infinitesimal amount, the work i...
Text Solution
|
- If the boundary of system moves by an infinitesimal amount, the work i...
Text Solution
|
- If the boundary of system moves by an infinitesimal amount, the work i...
Text Solution
|
- Standard Gibb's energy of reaction (Delta(r )G^(@)) at a certain temp...
Text Solution
|
- Standard Gibb's energy of reaction (Delta(r )G^(@)) at a certain temp...
Text Solution
|
- Standard Gibb's energy of reaction (Delta(r )G^(@)) at a certain temp...
Text Solution
|
- Standard Gibb's energy of reaction (Delta(r )G^(@)) at a certain temp...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following reaction : CO(g)+2H(2)(g)iffCH(3)OH(g) Give...
Text Solution
|
- Enthalpy of neutralization is defined as the enthalpy change when 1 mo...
Text Solution
|
- Enthalpy of neutralzation is defined as the enthalpy change when 1 mol...
Text Solution
|
- Enthalpy of neutralzation is defined as the enthalpy change when 1 mol...
Text Solution
|
- Gibbs Helmholtz equation relates the enthalpy, entropy and free energy...
Text Solution
|
- Gibbs Helmholtz equation relates the enthalpy, entropy and free energy...
Text Solution
|
- Gibbs Helmholtz equation relates the enthalpy, entropy and free energy...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the intensive quantities from the following : (a)Enthalpy ...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the extensive quantities from the following :
Text Solution
|
- Identify the state functions from the following :
Text Solution
|