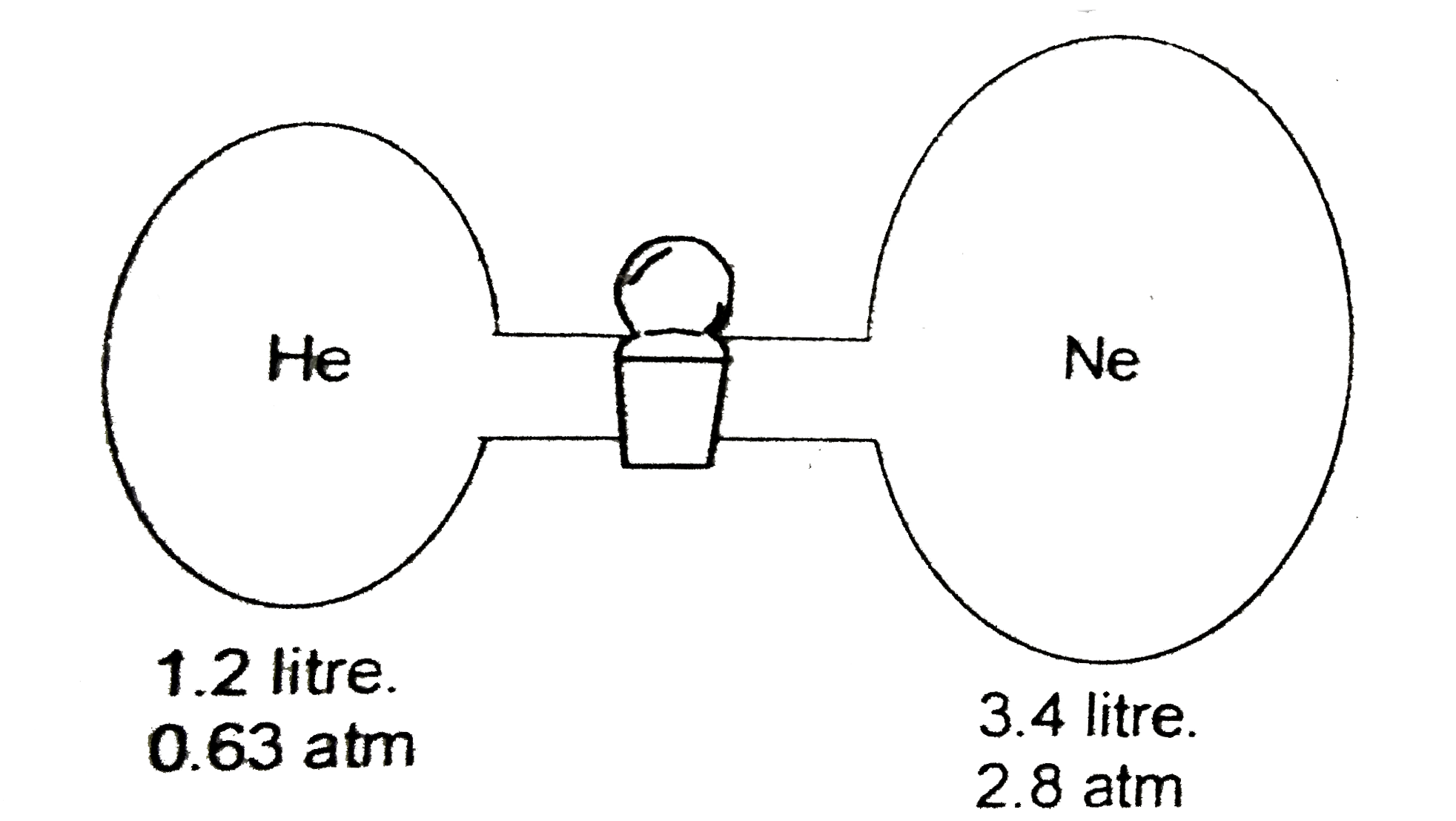
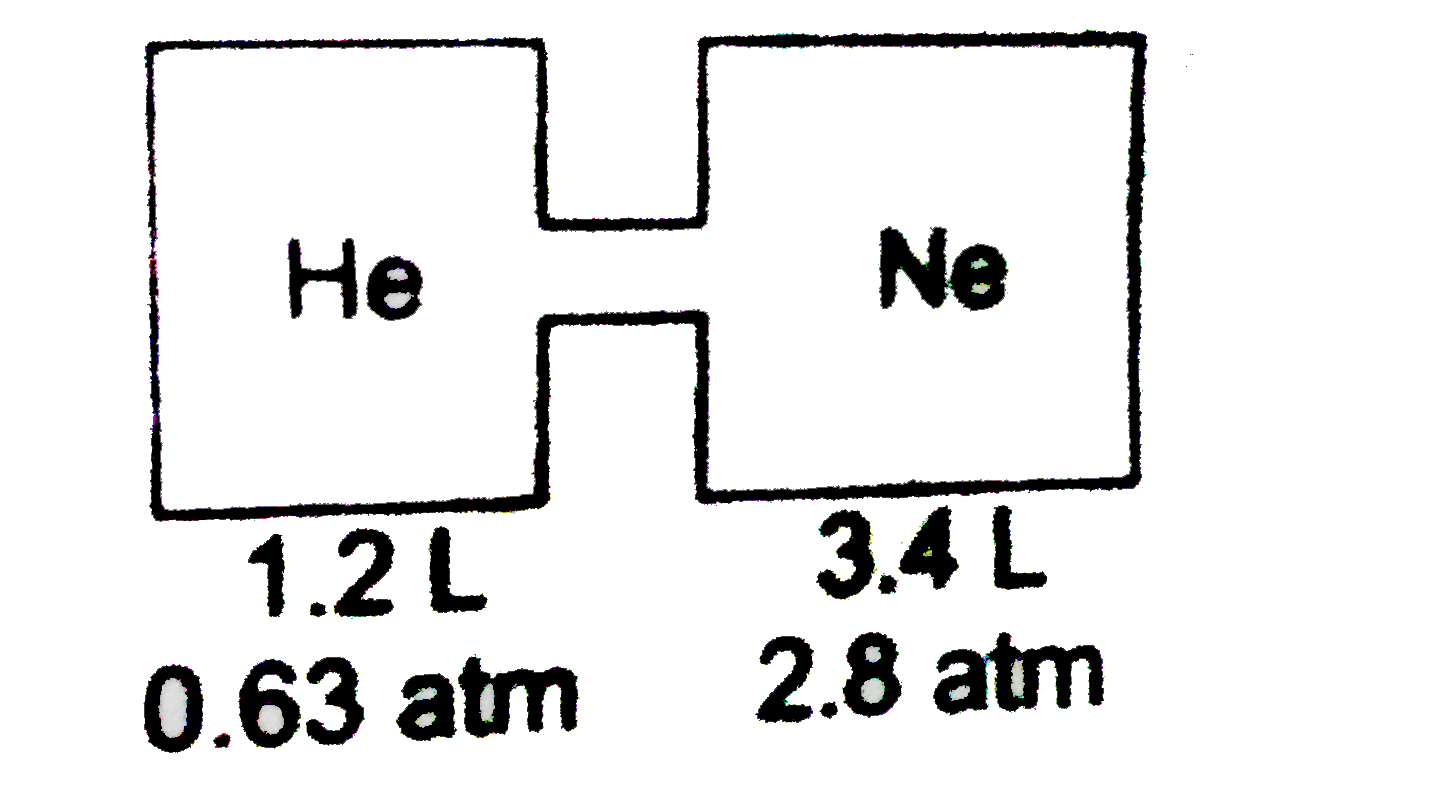A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NARENDRA AWASTHI ENGLISH-GASEOUS STATE-Subjective problems
- Consider the following apparatus. Calculate the partical pressure of H...
Text Solution
|
- A bubble of gas released at the bottom of a lake increases to four t...
Text Solution
|
- A gaseous mixture containing equal mole sof H(2),O(2) and He is subjec...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a gas changed from its initial state (15L,2 atm) to final ...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of an ideal gas undergoes the following process. Given that ...
Text Solution
|
- 1 mole of a diatomic gas present in 10 L vessel at certain temperature...
Text Solution
|
- The graph of compressibility factor (Z) vs. P for one mole of a real g...
Text Solution
|
- Under the identical conditions of temperature, the density of a gas X...
Text Solution
|
- The time for a certain volume of a gas A to diffuse through a small ho...
Text Solution
|
- Excess F(2)(g) reacts at 150^(@)C and 1.0 atm pressure with Br(2)(g) t...
Text Solution
|
- Initially bulb "a" contained oxygen gas at 27^(@)C and 950 mm of Hg an...
Text Solution
|
- Air is trapped in a horizontal glass tube by 36 cm mercury column as s...
Text Solution
|
- A flask containing air at 107^(@)C and 722 mm of Hg is cooled to 100 K...
Text Solution
|
- If an ideal gas at 100 K is heated to 109 K in a rigid container, the ...
Text Solution
|
- The van der Waals' constantes for a gas are a=3.6 atmL^(2)mol^(-2),b=0...
Text Solution
|
- A flask has 10 molecules out of which four molecules are moving at 7 m...
Text Solution
|