In figure, the optical fiber is `I=2m` long and has a diameter of `d=20 mum`. If a ray of light is incidnet on one end of the fiber at angle `0_(1)=40^(@)C`, the number of reflections if makes before emerging from the other and is close to:
(refractive index of fiber is `1.31` and `sin40^(@)=0.64`)
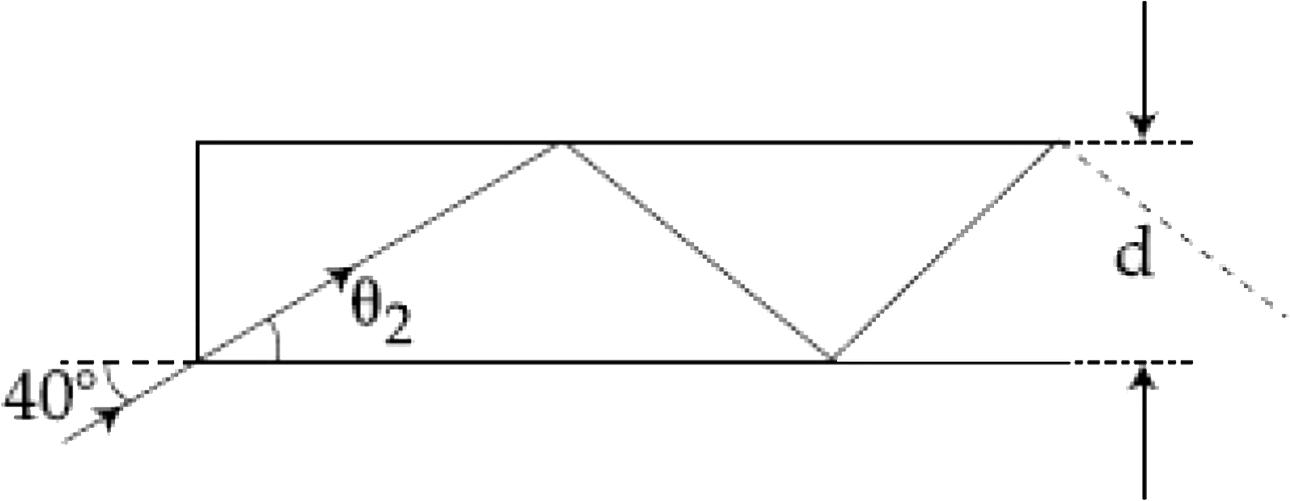
In figure, the optical fiber is `I=2m` long and has a diameter of `d=20 mum`. If a ray of light is incidnet on one end of the fiber at angle `0_(1)=40^(@)C`, the number of reflections if makes before emerging from the other and is close to:
(refractive index of fiber is `1.31` and `sin40^(@)=0.64`)

(refractive index of fiber is `1.31` and `sin40^(@)=0.64`)

A
`55000`
B
`66000`
C
`45000`
D
`57000`
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
B
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Two plane mirrors each 1.6 m long, are facing each other. The distance between the mirrors is 20 cm. A light incident on one end of one of the mirrors at an angle of incidence of 30^(@) . How many times is the ray reflected before it reaches the other end?
P is small angled prism of angle 3^(@) made of a material of refractive index 1.5 . A ray of light is incident normally to the mirror as shown in figure. M is a plane mirror. The angle of deviation for the ray reflected from the mirror M with respect to the incident ray is : A. 4.5^(@) B. 175.3^(@) C. 177^(@) D. 178.5^(@)
An optical fiber has index of refraction n=1.40 and diameter d=100 mu m . It is surrounded by air. Light is sent into the fiber along the axis as shown in figure. If smallest outside radius R permitted for a bend in the fiber for no light to escape is given by 50 x ("in" mu m) fill value of x.
What is the least radius through which an optical fiber of core diameter 0.05 mm may be bent (as shown in figure) without serious loss of light? The refractive index of the core is 1.6 and that of cladding is 1.5.
A solenoid is 1.5 m long and its inner diameter is 4.0 cm . It has three layers of windings of 1000 turns each and carries a current of 2.0 amperes. The magnetic flux for a cross-section of the solenoid is nearly
In a Young's double slit experiment, a parallel beam containing wavelengths lambda_(1)=4000Å and lambda_(2)=5600Å is incident at an angle phi=30^(@) on a diaphragm having narrow slits at separation d=2mm. The screen is placed at a distance D =40 cm from the slits. a mica slab of thickness t=5mm is placed in front of one of the slits and whole of the apparatus is submerged in water. if the central bright fringe is observed at C, determine. (i) The refractive index of the slab (ii) The distance of first black line from C both wavelength are in air. take mu_(w)=4/3
From the focus (-5,0) of the ellipse (x^(2))/(45)+(y^(2))/(20) =1 , a ray of light is sent which makes angle cos^(-1)((-1)/(sqrt(5))) with the positive direction of X-axis upon reacting the ellipse the ray is reflected from it. Slope of the reflected ray is
A ray of light travelling in air is incident at angle of incidence I~~90^(@) on a long rectangular slab of a transparent medium of thickness y_(0) . The medium has a variable refractive index of mu(x)=sqrt(1+ke^(2x//a),xge0 wher a is a positive constant
Pulfrich refractometer is used to measure the refractive index of solids and liquid. It consist of right angled prism. A having its two faces perfectly plane. One of the face is horizontal and the other is vertical as shown is figure. The solid B whose refractive index is to be determined is taken having two faces cut perpendicular to one another. Light is incident in a direction parallel to the horizontal surface so that the light entering the prism A is at critical angle C. Finally, it emerges from the prism at an angle i. Let the refractive index of the solid be mu and that of the prism A be mu_(0) (which is known). Here mu_(0)gtmu and by measuring i, mu can be determinged. Q. Refractive index of the solid (mu) in terms of mu_(0) and i is
This interference film is used to measure the thickness of slides, paper, etc. The arrangement is as shown in fig. For the sake of clarity, the two strips are shown thick. Consider the wedge formed in between strips 1 and 2. If the interference pattern because of the two waves reflected from wedge surface is observed, then from the observed data we can compute thickness of paper, refractive index of the medium filled in wedge, number of bonds formed, etc. Considre the strips to be thick as compared to wavelength of ligth and light is incident normally. Neglect the effect due to reflection from top surface of strip 1 and bottom surface of strip 2. Take L = 5 cm and lambda_(air) = 40 nm . Consider an air wedge formed by two glass plates. having refractive index 1.5 by placing a piece of paper of thickness 20 mm. Determine the number of dark bands formed.