A ball is through vertically up (taken as +z-axis) from the ground. The correct momentum-height (p-h) diagram is :
A ball is through vertically up (taken as +z-axis) from the ground. The correct momentum-height (p-h) diagram is :
A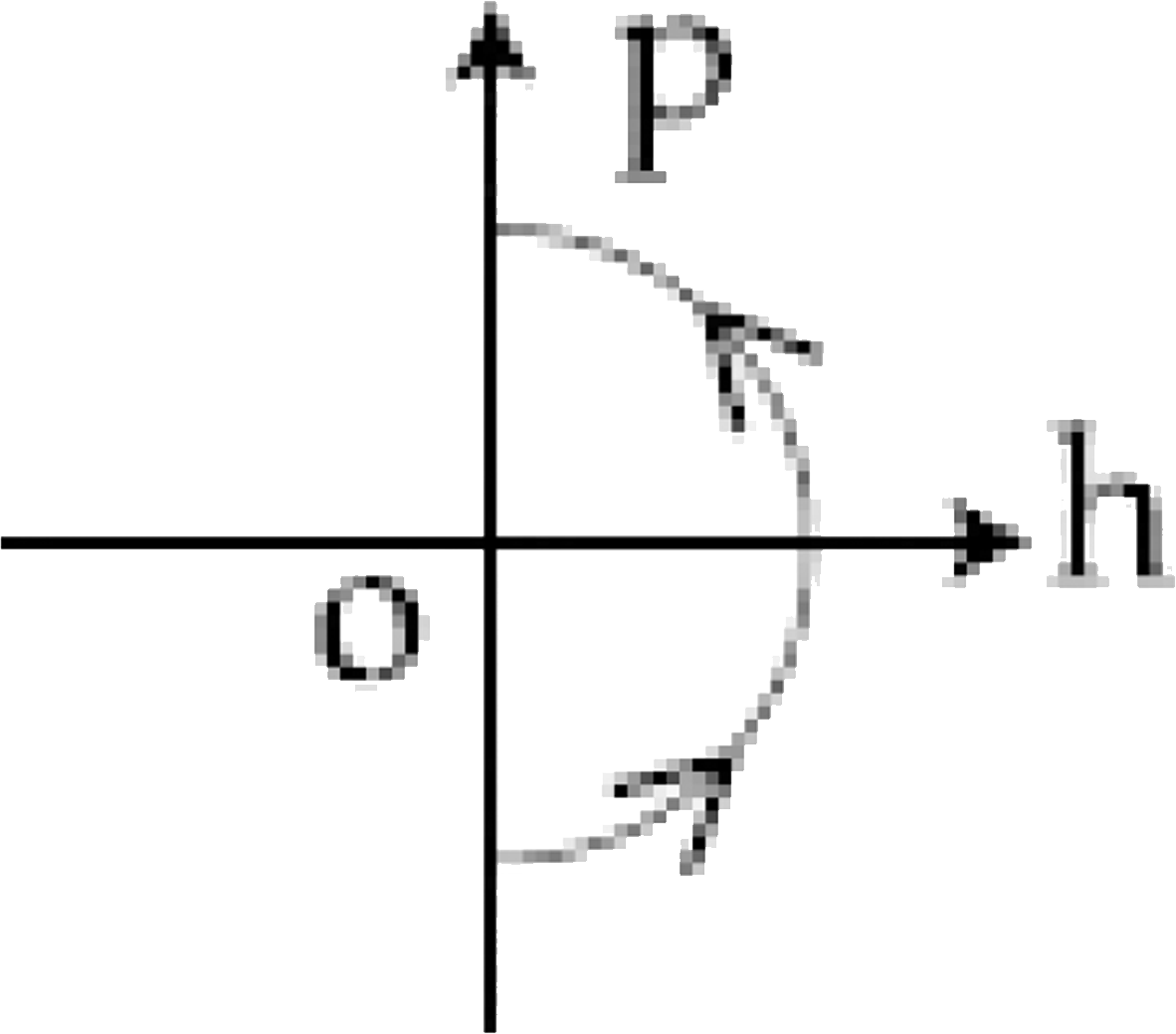

B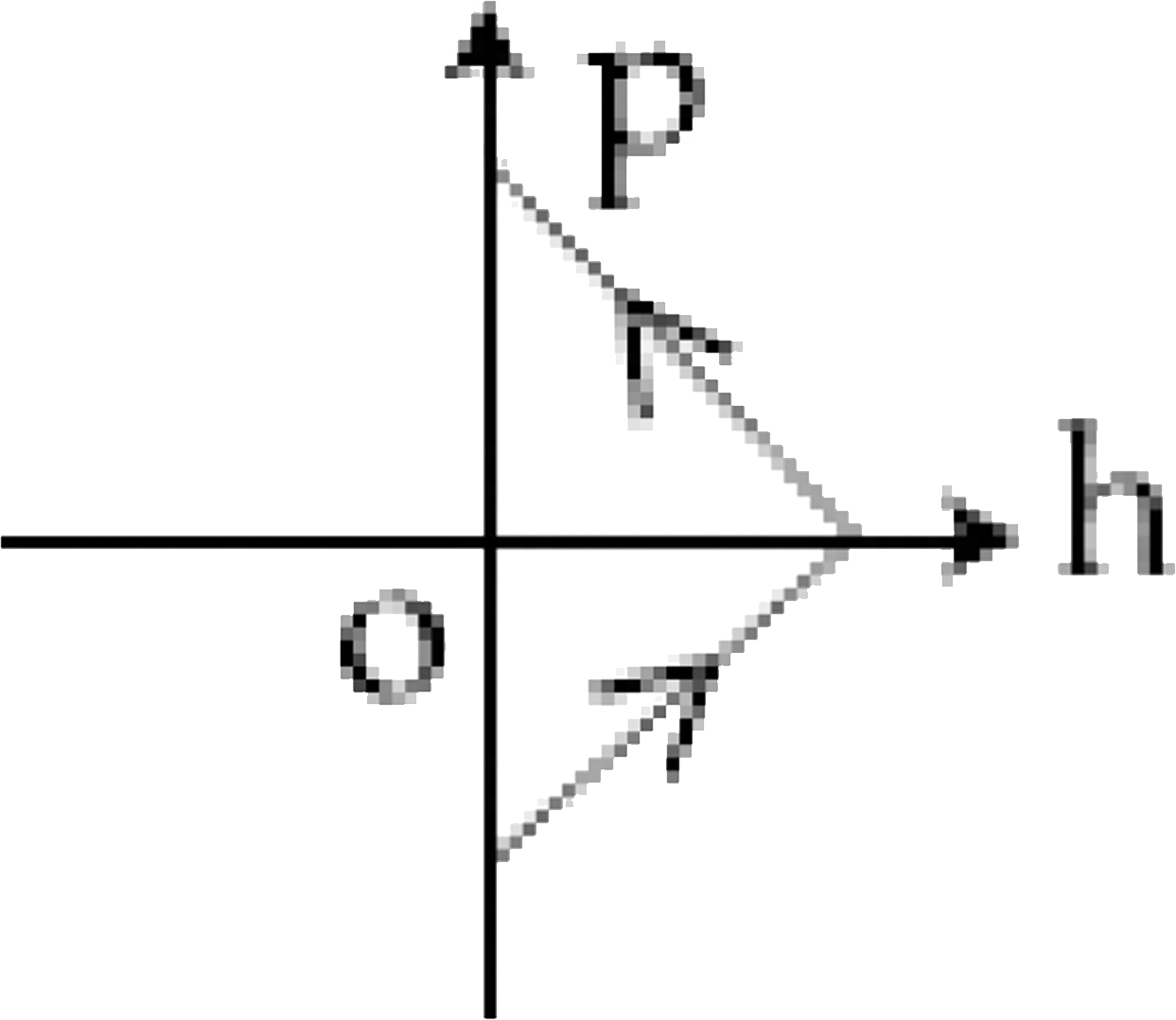

C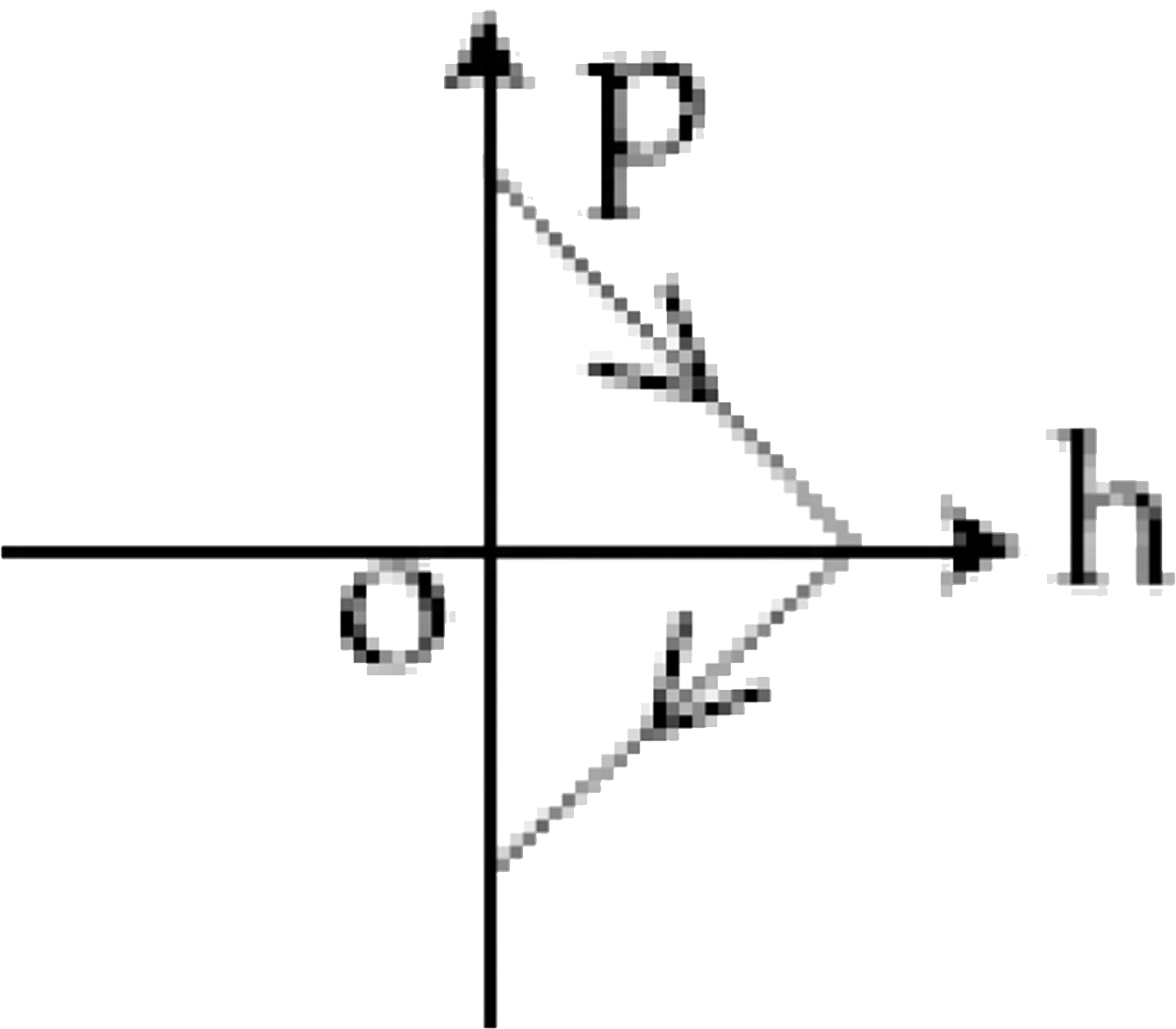

D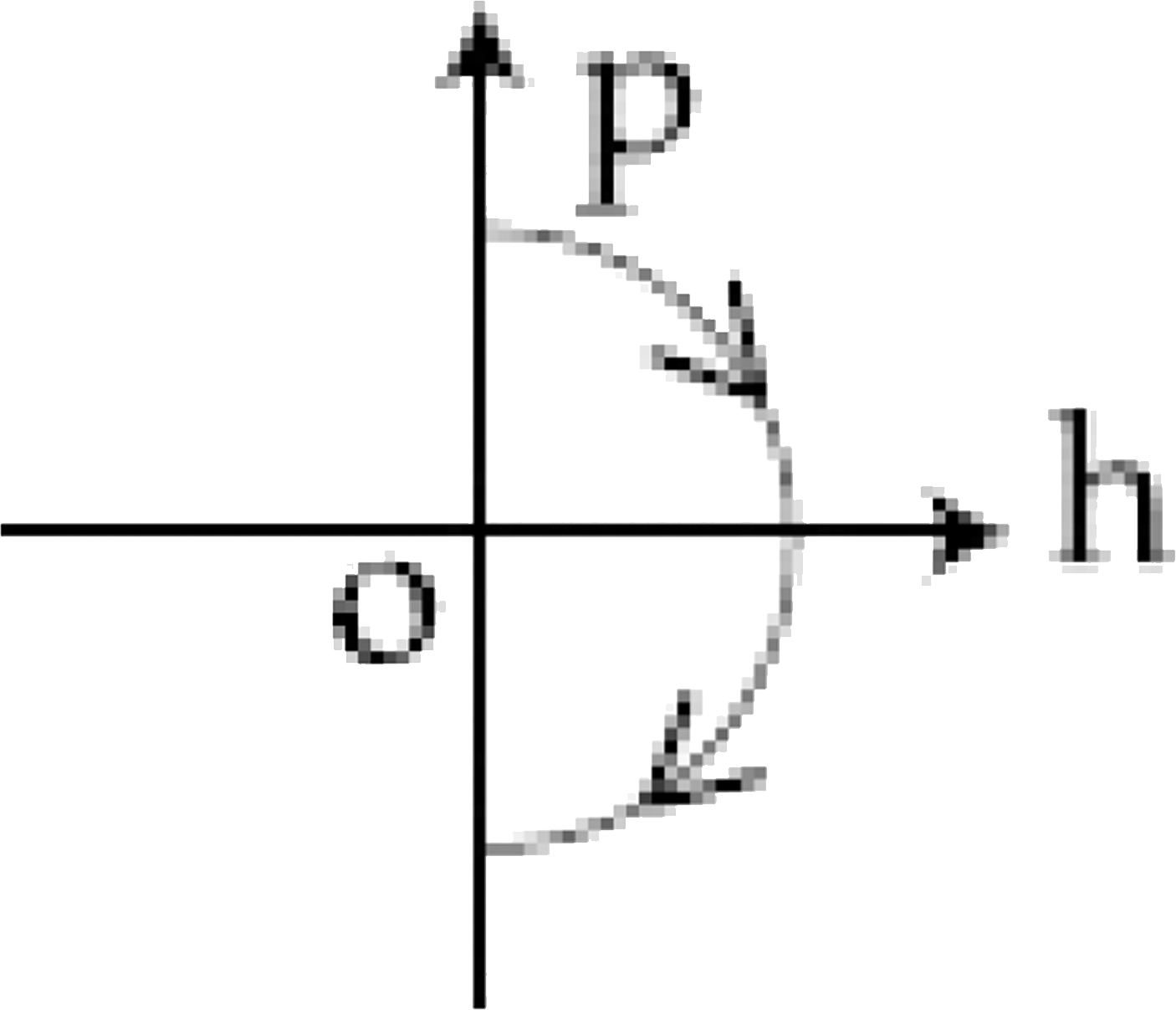
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
To solve the problem of determining the correct momentum-height (p-h) diagram for a ball thrown vertically upwards, we can follow these steps:
### Step-by-Step Solution:
1. **Understanding Initial Conditions**:
- A ball is thrown vertically upwards from the ground with an initial velocity \( v_0 \).
- The momentum \( p \) of the ball at the initial height (ground level, \( h = 0 \)) is given by:
\[
p = m \cdot v_0
\]
- Since the ball is moving upwards, the momentum is positive.
2. **Analyzing Motion**:
- As the ball rises, it experiences a gravitational force acting downwards, which causes its velocity to decrease.
- At the maximum height \( h \), the velocity becomes zero, and thus the momentum also becomes zero:
\[
p = 0 \quad \text{at} \quad h = h_{\text{max}}
\]
3. **Momentum as a Function of Height**:
- The relationship between momentum and height can be derived from the equations of motion. Using the equation:
\[
v^2 = u^2 - 2gh
\]
- Here, \( v \) is the final velocity (which becomes zero at maximum height), \( u \) is the initial velocity \( v_0 \), and \( g \) is the acceleration due to gravity.
- Rearranging gives:
\[
0 = v_0^2 - 2gh_{\text{max}} \implies h_{\text{max}} = \frac{v_0^2}{2g}
\]
4. **Momentum-Height Relationship**:
- The momentum can be expressed as:
\[
p = m \cdot v = m \cdot \sqrt{v_0^2 - 2gh}
\]
- Squaring both sides gives:
\[
p^2 = m^2(v_0^2 - 2gh)
\]
- This shows that \( p^2 \) is a linear function of \( h \), indicating that the momentum decreases as height increases.
5. **Graphing the Relationship**:
- At \( h = 0 \), \( p \) is maximum (\( p = m v_0 \)).
- As \( h \) increases to \( h_{\text{max}} \), \( p \) decreases to zero.
- After reaching maximum height, as the ball falls back down, momentum becomes negative, increasing in magnitude until it reaches \( -m v_0 \) when it returns to the ground.
6. **Identifying the Correct Option**:
- The correct momentum-height graph will show momentum starting at a maximum positive value at \( h = 0 \), decreasing to zero at maximum height, and then becoming negative as the ball falls back down.
- This behavior corresponds to option D.
### Final Answer:
The correct momentum-height (p-h) diagram is **option D**.
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A bal is thrown vertically upwards from the ground. It crosses a point at the height of 25 m twice at an interval of 4 secs. The ball was thrown with the velocity of
A ball is thrown vertically upwards from the ground. If T_1 and T_2 are the respective time taken in going up and coming down, and the air resistance is not ignored, then
An open elevator is ascending with constant speed v=10m//s. A ball is thrown vertically up by a boy on the lift when he is at a height h=10m from the ground. The velocity of projection is v=30 m//s with respect to elevator. Find (a) the maximum height attained by the ball. (b) the time taken by the ball to meet the elevator again. (c) time taken by the ball to reach the ground after crossing the elevator.
A ball of mass 'm' is thrown vertically up-ward from the ground and reached a height 'h' before momentarily coming to rest , If 'g' is acceleration due to gravity . What is the impulse received by the ball due to gravity force during its flight ? (neglect air resistance )
A body is thrown vertically upward from a point A 125 m above the ground. It goes up to a maximum height of 250 m above the ground and passes through A on its downward journey. The velocity of the body when it is at a height of 70 m above the ground is (g=10 m//s^(2))
A ball is thrown vertically upwards from the top of tower of height h with velocity v . The ball strikes the ground after time.
A ball of mass m is thrown vertically up with an initial velocity so as to reach a height h.The correct statement is :
A particle is thrown vertically upward with a speed u from the top of a tower of height h from ground level, If after first impact with ground it just reaches to height h from ground the coeffecient of restitution for the collision is :-
A body falling a vertically up with initial velocity 52 m/s from the ground passes twice a point at h height above at an interval of 10 s. The height h is (g=10m//s^(2))
A stone projected vertically upwards from the ground reaches a maximum height h . When it is at a height (3h)//(4) , the ratio of its kinetic and potential energies is