The anode vollage of a photocell is kept fixed . The wavelength `lambda `of the light falling on the cathode varies as follows
The anode vollage of a photocell is kept fixed . The wavelength `lambda `of the light falling on the cathode varies as follows
A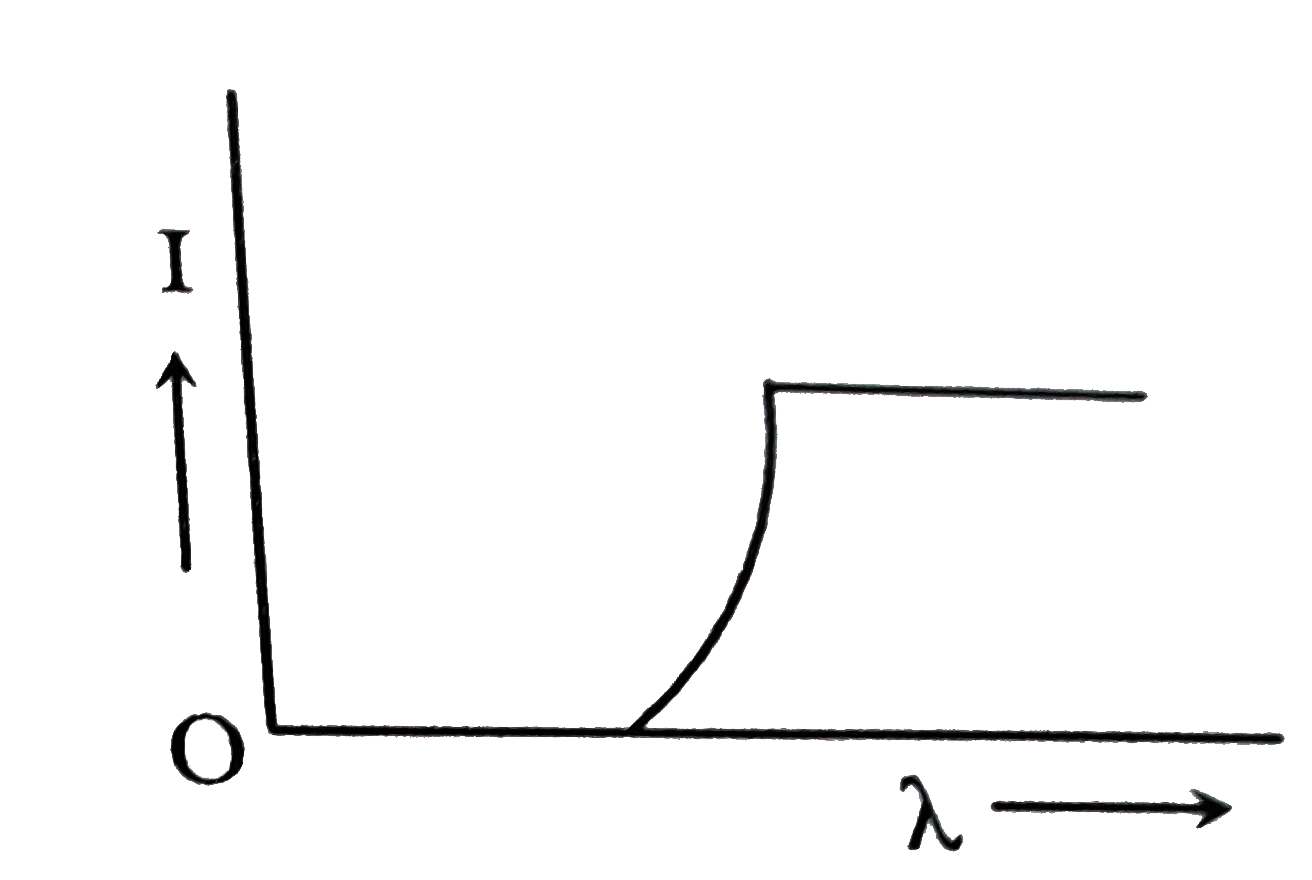

B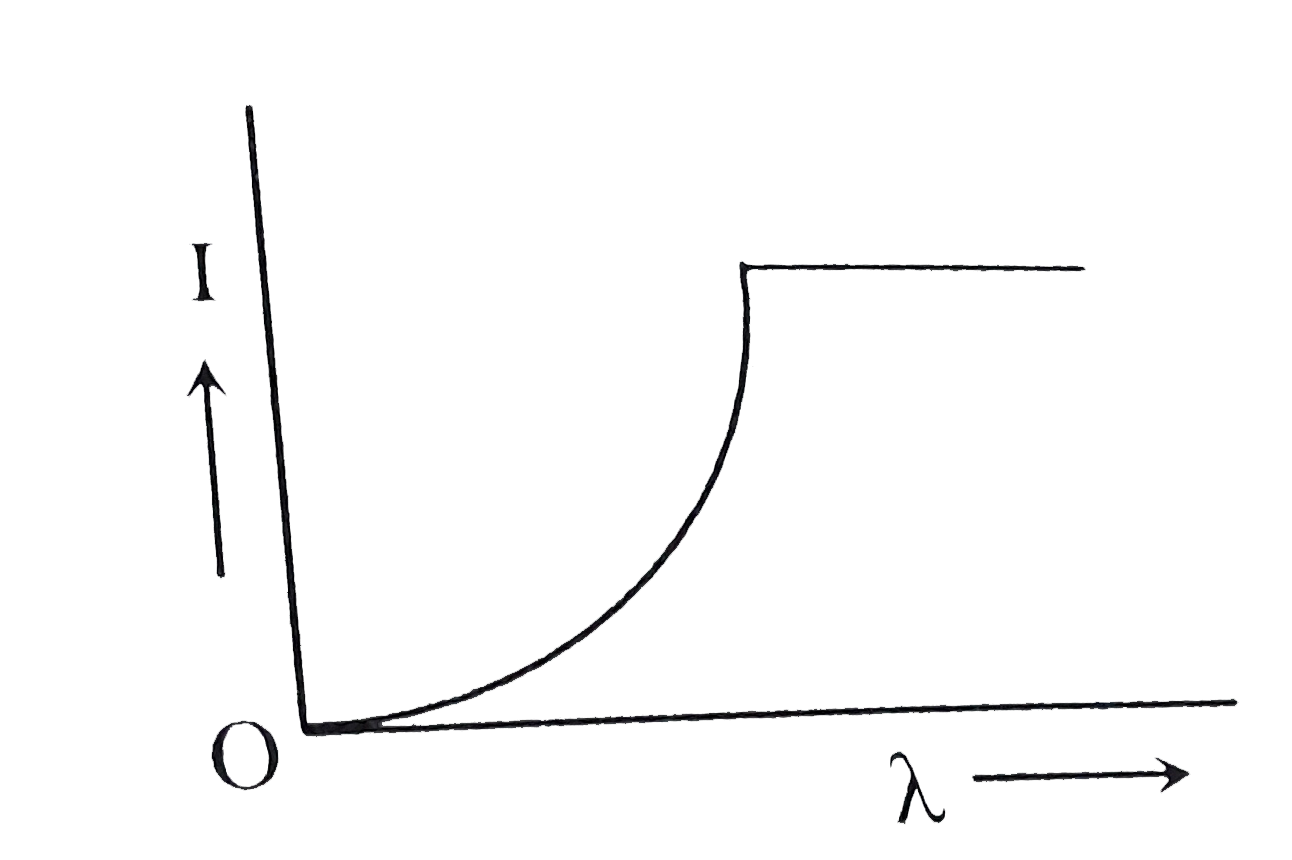

C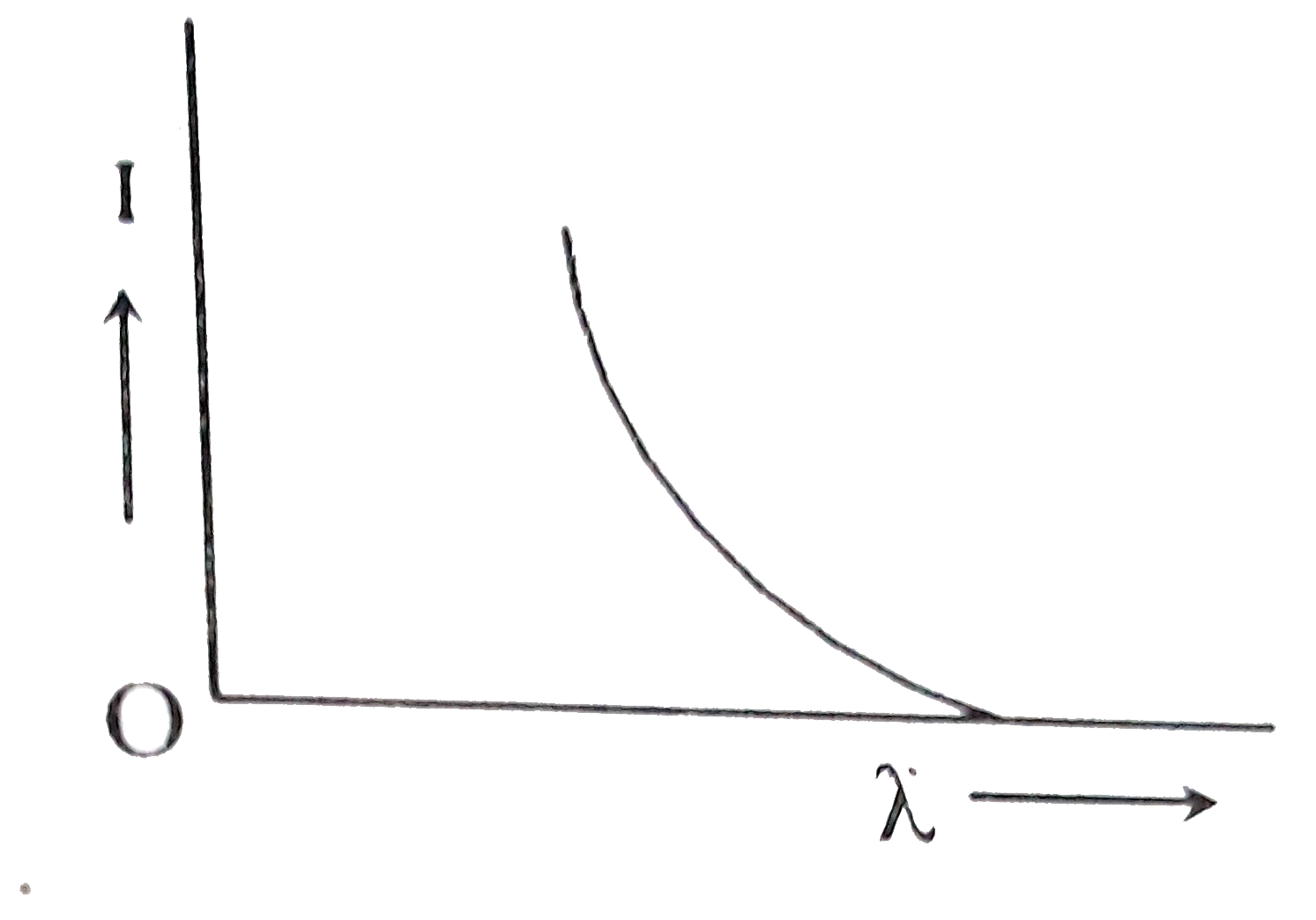

D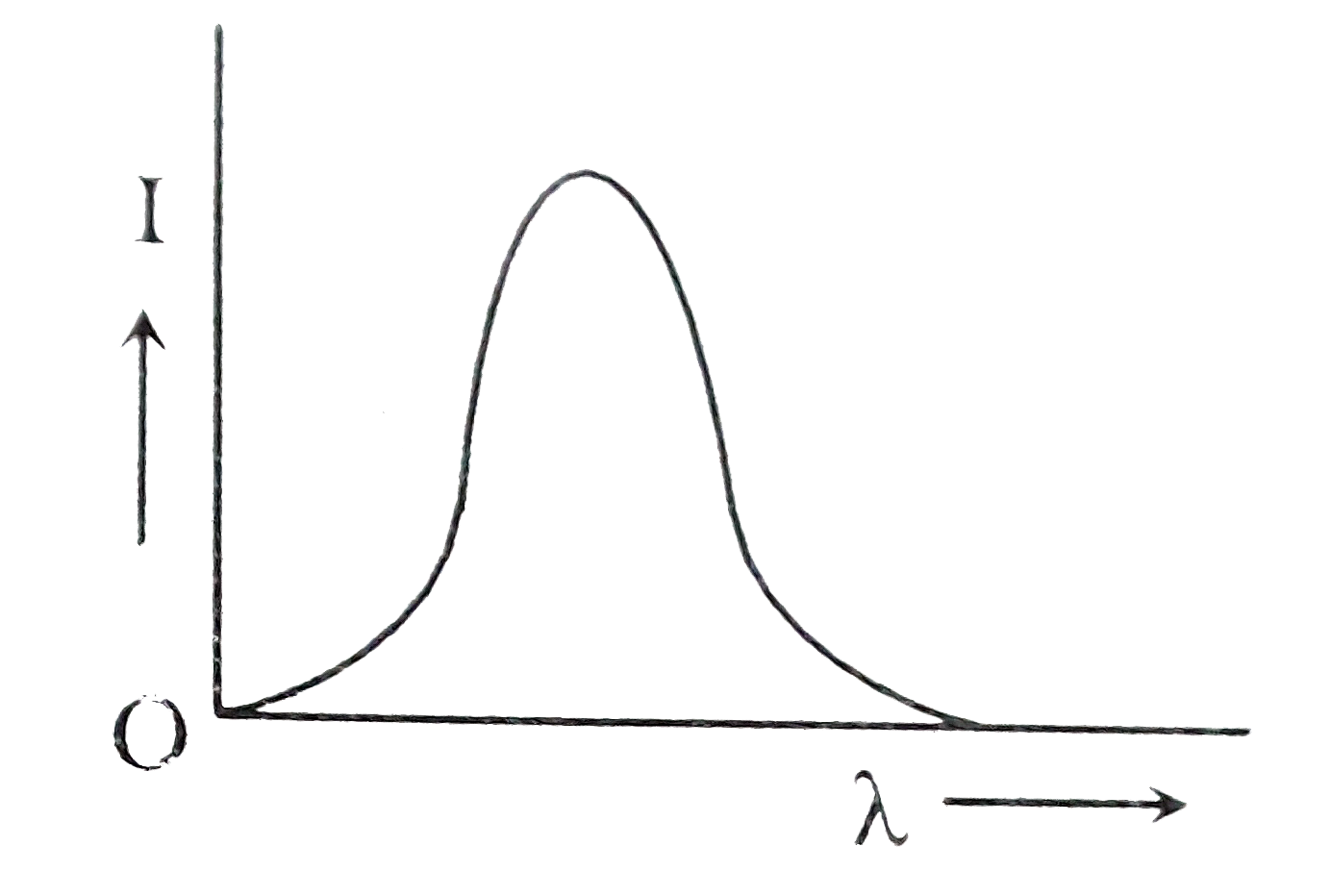

Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
To solve the problem, we need to analyze how the current in a photocell varies with the wavelength of light falling on the cathode. Here’s the step-by-step solution:
### Step 1: Understand the relationship between current and intensity
The current (I) in a photocell is directly proportional to the intensity (I) of the light falling on the cathode. This can be expressed as:
\[ I \propto I \]
### Step 2: Relate intensity to wavelength
The intensity of light is defined as the energy per unit time per unit area. The energy of a photon is given by the equation:
\[ E = \frac{hc}{\lambda} \]
where:
- \( h \) is Planck's constant,
- \( c \) is the speed of light,
- \( \lambda \) is the wavelength of the light.
### Step 3: Express intensity in terms of wavelength
If we consider the intensity (I) to be proportional to the energy, we can write:
\[ I \propto \frac{1}{\lambda} \]
This indicates that as the wavelength increases, the intensity decreases.
### Step 4: Relate current to wavelength
Since the current is directly proportional to the intensity, we can conclude:
\[ I \propto \frac{1}{\lambda} \]
This means that the current is inversely proportional to the wavelength of the light falling on the cathode.
### Step 5: Conclusion
From our analysis, we find that:
- If the wavelength (\( \lambda \)) increases, the current (I) decreases.
- Conversely, if the wavelength decreases, the current increases.
Thus, the correct answer is that the current is inversely proportional to the wavelength.
### Final Answer:
The current in the photocell is inversely proportional to the wavelength of the light falling on the cathode.
---
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
The anode voltage of a photo cell is kept fixed. The wavelength lamda of the light falling on the cathode is gradually changed. The plate current I of the photo cell varies as follows
The stopping potential in a photoelectric experiment is linearly related to the inverse of the wavelength (1/lambda) of the light falling on the cathode. The potential difference applied across an X-ray tube is linearly related to the inverse of the cutoff wavelength (1/lambda) of the X-ray emitted. Show that the slopes of the lines in the two cases are equal and find its value.
The maximum kinetic energy of photoelectron is doubled when the wavelength of light incident on the photosensitive changes from lambda_1 to lambda_2 . Deduce expression for the threshold wavelength and work function for metals in terms of lambda_1 and lambda_2
If lambda_(0) is the threshold wavelength for photoelectric emission. lambda wavelength of light falling on the surface on the surface of metal, and m mass of electron. Then de Broglie wavelength of emitted electron is :-
A vacuum photocell consists of a central cathode and an anode. The internal surface is silver of work function 4.5 eV. The contact potential difference between the electrodes equals to 0.6 V. The photocell is illuminated by light of wavelength 2.3xx10^-7 m. a. What retrading potential difference should be applied between electrodes of the photocell for the photocurrent to drop to zero? b. If a retarding potential of 1V is applied between electrodes at what limiting wavelength lamda of light incident on the cathode will on the cathode will the photoelectric effect begin?
Electrons are emitted from the cathode of a photocell of negligible work function, when photons of wavelength lamda are incident on it. Derive the expression for the de Broglie wavelength of the electrons emitted in terms of the wavelength of the incident light
Two identical metal plates show photoelectric effect by a light of wavelength lambda_A falling on plate A and lambda_B on plate B (lambda_A=2lambda_B) . The maximum kinetic energy is
A source emits monochromatic light of frequency 5.5xx10^(14) Hzat a rate of 0.1 W. Of the photons given out, 0.15% fall on the cathode of a photocell which gives a current of 6muA in an extrnal circuit. (a) Find the enrgy of a photon. (b) Find the number of photons leaving the source per second. (C) Find the percentage of the photons falling on the cathode which produce photoelectrons.
In young's double slit experiment using monochromatic light of wavelengths lambda , the intensity of light at a point on the screen with path difference lambda is M units. The intensity of light at a point where path difference is lambda//3 is
Photoelectric work- function of a metal is 1 eV. Light of wavelength lambda = 3000 Å falls on it. The photoelectrons come out with maximum velocity