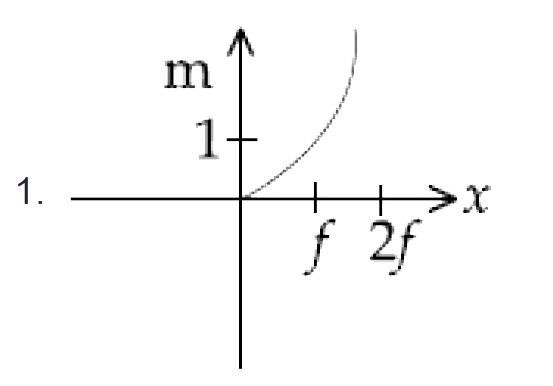
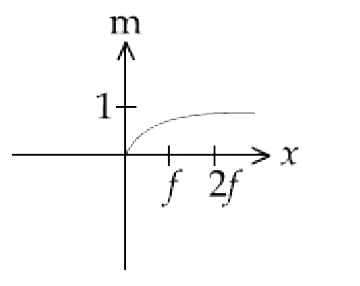
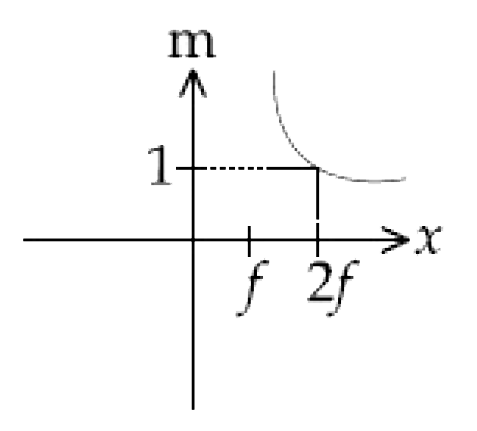
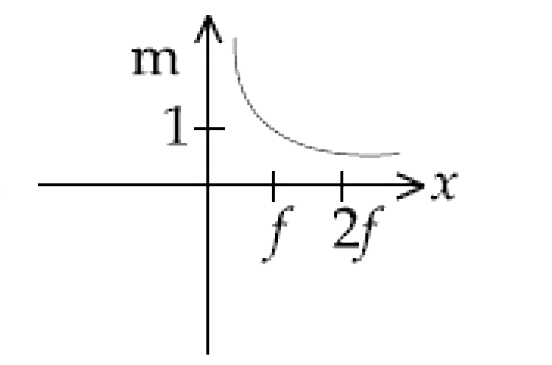
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
JEE MAINS PREVIOUS YEAR ENGLISH-JEE MAIN-All Questions
- A plane electromagnetic wave of frequency 25 GHz is propagating in vac...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum is being used to determine the value of gravitationa...
Text Solution
|
- An object is moving away from concave mirror of focal length f startin...
Text Solution
|
- Two square plates of side 'a' are arranged as shown in the figure. The...
Text Solution
|
- Velocity of a wave in a wire is v when tension in it is 2.06 × 10^4 N....
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves so that its position vector is given by vec r = cos o...
Text Solution
|
- A galvanometer having a coil resistance 100 Omega given full scale ...
Text Solution
|
- As shown in the figur a battery of emf in is conneced to an inductor...
Text Solution
|
- Output at terminal Y of given logic circuit.
Text Solution
|
- A Carnot engine, having an efficiency of eta= 1/10 as heat engine, is ...
Text Solution
|
- If the wavelength of the first line of the Balmer series of hydrogen i...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is dropped from height h = 100 m, from surface of a planet....
Text Solution
|
- The series combination of two batteries both of the same emf 10 V, bu...
Text Solution
|
- When two non reactive samples at different temperatures are mixed in a...
Text Solution
|
- Two electromagnetic waves are moving in free space whose electric fiel...
Text Solution
|
- Consider an infinitely long current carrying cylindrical straight wire...
Text Solution
|
- Consider, two ideal diatomic gases A and B at some temperature T. Mole...
Text Solution
|
- Three waves of same intensity (I0) having initial phases 0, pi/4 , - ...
Text Solution
|
- In the given circuit diagram, a wire is joining points B and D. The cu...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is revolving around a planet in a circular orbit ...
Text Solution
|