A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
JEE MAINS PREVIOUS YEAR ENGLISH-JEE MAIN-All Questions
- A block of mass m start slipping from top of inclined plane at B and c...
Text Solution
|
- Stopping potential of emitted photo electron is V when monochromatic l...
Text Solution
|
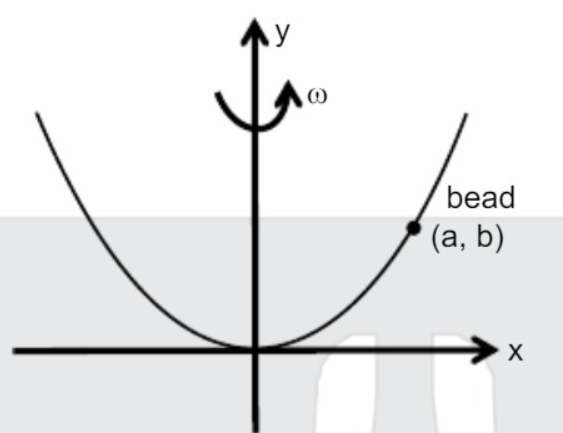
- Angular velocity of smooth parabolic wire y = 4c(x)^(2) about axis of ...
Text Solution
|
- Fundamental frequency of two identical strings x and y are 450Hz and 3...
Text Solution
|
- In a standard YDSE slit width is 1mm and distance of screen from the s...
Text Solution
|
- A proton enter in a uniform magnetic field of 2.0 mT at an angle of 60...
Text Solution
|
- Amplitude of carrier wave and message wave are 5 unit and 3 unit resp....
Text Solution
|
- A rod is heated from 0^@ to 10^@, its length is changed by 0.02%. By w...
Text Solution
|
- Magnetic moment of the lap
Text Solution
|
- If area(A), time(T) and momentum(P) is assume as fundamental quantitie...
Text Solution
|
- vecE & vecB in an electromagnetic wave oscillate along the directionha...
Text Solution
|
- A charge Q is distributed over two concentric conducting thin spherica...
Text Solution
|
- A capillary of radius 0.15mm is dipped in liquid of density 'rho' = 66...
Text Solution
|
- In given potentiometer circuit 1.02 V is balanced at 5.1cm from A. Fin...
Text Solution
|
- In hydrogen atom electron jumps from (n+1)th state to nth state the fr...
Text Solution
|
- Displacement time graph of particle performing SHM is as shown in figu...
Text Solution
|
- A closed box contains an ideal gas if temperature of gas increased whi...
Text Solution
|
- R1 = R2 = R3 = R4 = 2ohm. Find voltage across capacitor at steady stat...
Text Solution
|
- Two disc having moment of inertias I1 & I2 and angle velocities omega1...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m and charge -q is projected from the origin with a...
Text Solution
|