A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
JEE MAINS PREVIOUS YEAR ENGLISH-JEE MAINS 2020-PHYSICS
- Train A and train B are running on parallel trackes in the opposite di...
Text Solution
|
- The least count of the main scale of vernier callipers is 1 mm. Its ve...
Text Solution
|
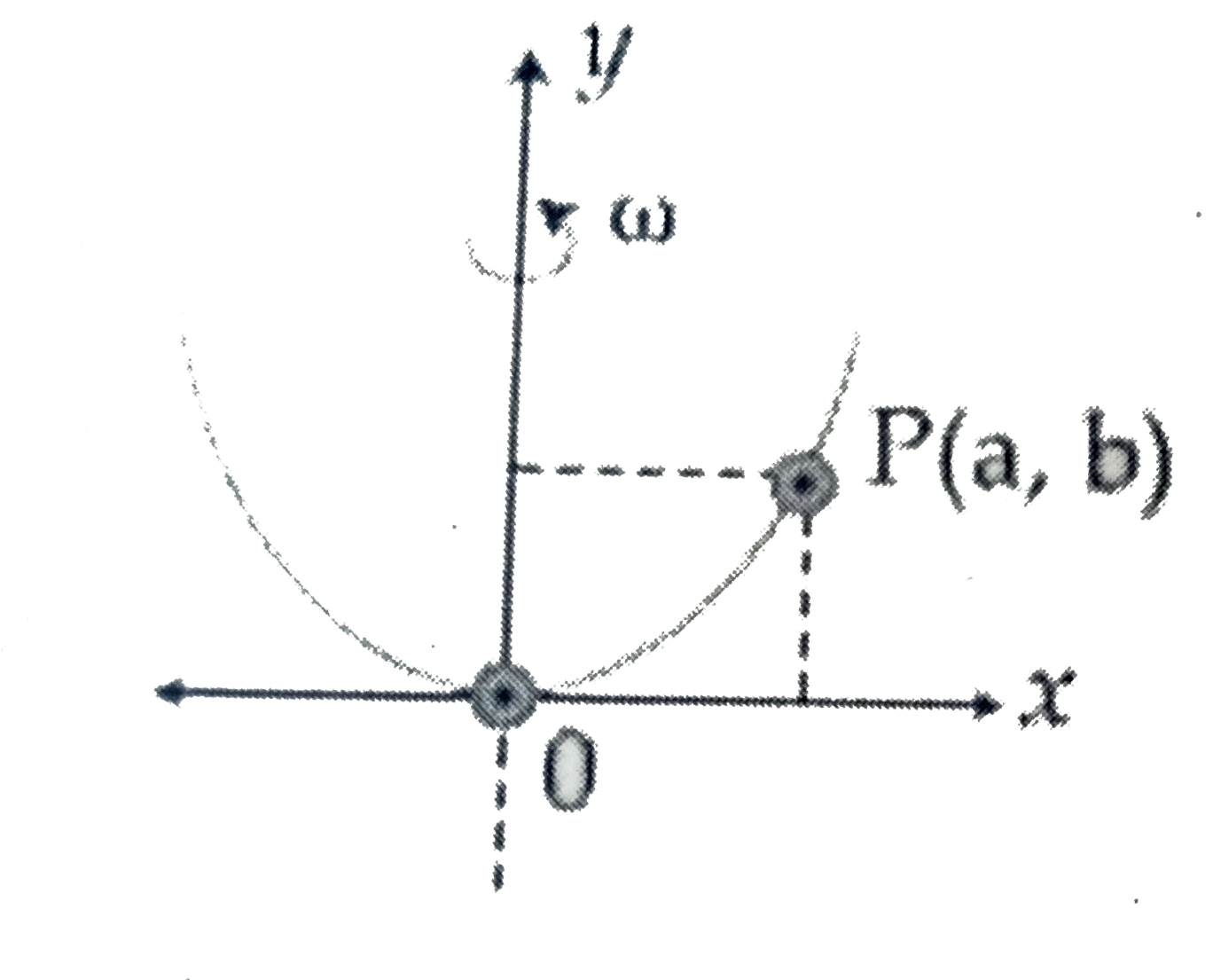
- A bead of mass m stays at point P (a,b) on a wire bent in the shape o...
Text Solution
|
- If speed (V),acceleration (A) and force (F) are considered as fundam...
Text Solution
|
- Magnetic materials used for making permanent magnets (P) and magnets i...
Text Solution
|
- When radiation of wavelength lambda is used to illuminate a metallic s...
Text Solution
|
- A 5 mu F capacitor is charged fully by a 220 V supply. It is then disc...
Text Solution
|
- A circular coil of radius 10 cm is placed in uniform magnetic field of...
Text Solution
|
- A small back starts slipping down from a point B on an inclined plane ...
Text Solution
|
- An engine takes in 5 moles of air at 20^(@)C and 1 atm, and compresses...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic sphere cools from 50^(@)C to 40^(@)C in 300 seconds. If the...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform magnetic field B exist in a direction perpedicuar to the...
Text Solution
|
- The mass density of a planet of radius R varie with the distance ...
Text Solution
|
- Two resistor 400 Omega and 800 Omega connected in series across...
Text Solution
|
- Two source of light emit X - rays of wavelenght 1 nm and visible ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of length 'l' is pivoted at one of itd ends on a vertica...
Text Solution
|
- Dimension of solar constant is:
Text Solution
|
- Concentric metallic hollow spheres of radii R and 4R hold charges Q1 a...
Text Solution
|
- A perfectily diamagnetic sphere has a small spherical cavity at its ce...
Text Solution
|
- Hydrogen ion and singly ionized helium atom are accelerated , from res...
Text Solution
|