A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
JEE MAINS PREVIOUS YEAR ENGLISH-JEE MAINS 2020-CHEMSITRY
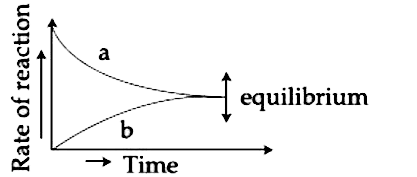
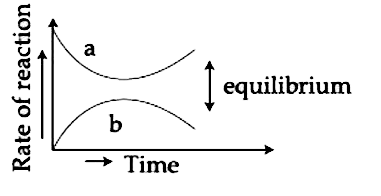
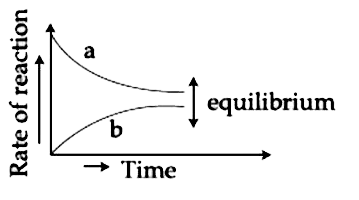
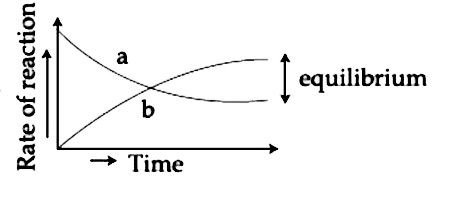
- For the equilibrium AhArrB , the variation of the rate of the forward ...
Text Solution
|
- The correct statement with respect to dinitrogen is :
Text Solution
|
- The major product obtained from the following reaction is :
Text Solution
|
- A solution of two components containing n1 moles of 1^(st) component a...
Text Solution
|
- The INCORRECT statement is :
Text Solution
|
- Consider the Assertion and Reason given below. Assertion (A) : Ethe...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following solutions in the decreasing order of pOH : (A...
Text Solution
|
- Among the sulphates of alkaline earth metals the solubilities of BeSO4...
Text Solution
|
- The major products of the following reaction are : CH3 -overset(CH...
Text Solution
|
- The major product of the following reaction is :
Text Solution
|
- A sample of toothpaste weighing 500 g, on analysis was found to contai...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds shows geometrical isomerism ?
Text Solution
|
- The set that contains atomic numbers of only transition elements , is ...
Text Solution
|
- The variation of equilibrium constant with temperature is given below ...
Text Solution
|
- Kraft temperature is the temperature :
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction Fe2N(s)+(3)/(2)H2(g)=2Fe(s)+NH3(g)
Text Solution
|
- The species that has a spin -only magnetic moment of 5.9 BM , is : (...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following Lanthanides element do not show stable +4 oxida...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following reaction A to P1, B to P2 , C to P3 , D to P4...
Text Solution
|
- In an estimation of bromine by Carius method , 1.6 g of an organic co...
Text Solution
|
- Potassium chlorate is prepared by the electrolusis of KCl in basic med...
Text Solution
|