Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SL ARORA-Work, Energy and power-EXERCISE
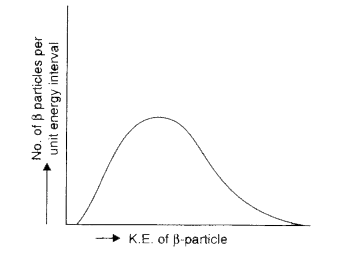
- Consider the decay of a free neutron at rest: ntop+e^(-) Show that the...
Text Solution
|
- What is the work done is crrrying a suitcase wighting 10 kg f on his h...
Text Solution
|
- What is the work done is crrrying a suitcase wighting 10 kg f on his h...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the amount of work done by a labourer who carries n bricks, ...
Text Solution
|
- A man moves on a straight horizontal road with a block of mass 2 kg i...
Text Solution
|
- A force F = (2hati-6 hatj) N is applied on a body. which is sliding ov...
Text Solution
|
- A force vecF=hat i+5 hat j+7 hat k acts on a particle and displaces it...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is acted upon by constant forces vecF=-2hati+3hatj+4hatk an...
Text Solution
|
- A man weighing 50kg f supports a body of 25 kg f on his head. What is ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain how work done by a variable force may be measured.
Text Solution
|
- A force F=(15+0.50x) acts on a particle in the X-directation ,where F ...
Text Solution
|
- A force F=a+b x acts on a particle in the X-direction, where a and b a...
Text Solution
|
- The relation between the displacement x and the time t for a body of m...
Text Solution
|
- Figrue shows the F-x graph. Where F is the force applied x is the dist...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate work done in moving the object from x=2 to x=3m from the gr...
Text Solution
|
- The momentum of a body of masss of 5kg is 500kg ms^(-1). Find the its...
Text Solution
|
- A bullet of mass 20g is found is found to pass two points 30cm apart i...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 2kg is resting on rough horizontal surface. A force 20N...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 2kg is resting on a rough horizontal surface. A force o...
Text Solution
|
- A electron and a proton are detected in a cosmic ray experiment, the e...
Text Solution
|
- A neutron of mass 1.66xx10^(-27)kg is moving with a speed of 7xx10^(5)...
Text Solution
|