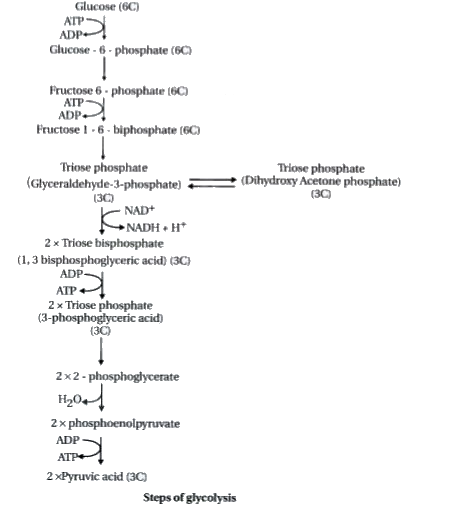
Definition : Glycolysis means the phase till formation of two molecules of pyruvic acid from one molecule of glucose takes place.
Origin : The term glycolysis has originated form the Greek words glucose form sugar and lysis for splitting .
The scheme of glycolysis was given by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyercdof and J. Parnas and is often referred to as the EMP pathway.
In anaerobic organisms, only glycolysis occurs. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and in this process undergoes partial oxidation to form two molecules of pyruvic acid .
In plants, this glucose is derived from sucrose .
which is the end product of photosynthesis or from storage carbohydrates. Both these monosaccharides readily enter the glycolytic pathway.
Glucose and fructose are phosphorylated to give rise to Glucose-6- phosphate by the activity of the enzyme hexokinase.
Glucose + ATP `overset("Hexokinase")to ` Glucose-6-Phosphate
This phosphorylated form of glucose then isomerises to produce fructose-6- phosphate.
Glucose-6- Phosphate `to` Fructose-6- Phosphate
Subsequent steps of metabolism of glucose and fructose are same.
In glycolysis, a chain of ten reactions, under the control of different enzymes, takes place to produce pyruvate from glucose.
Now fructose-6- phosphate is converted into fructose-1, 6 -biphosphate in presence of ATP.
ATP is utilised at two steps. First in the conversion of glucose into glucose 6-phosphate an in second step the conversion of fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 1, e-biphosphate.
Now the fructose 1,6-biphosphate is split into dihydroxyacetone phosphate and 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde (PGAL).
Fructose 1, 6-Biphosphate `to ` DHAP(3G) + PGAL (3G)
There is one step where NADH + `H^(+)` is formed from `NAD^(+)`, this is when 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde is converted to 1,3-biphosphoglycerate (BPGA).
3-phosphoglyceraldehyde `to` 1,3-biphosphoglycerate + NADH `+ H^(+)`
Two redox-equivalents are removed (in the form of hydrogen atoms) from PGAL, and transferred to a molecule of `NAD^(+)`
PGAL is oxidised and with inorganic phosphate to get converted into BPGA.
The conversion of BPGA to 3-phosphoglyceric acid (PGA) ,is also an energy yielding process. This energy is trapped by the formation of ATP
Another ATP is synthesised during the conversion of PEP to pyruvic acid .
(Formation of ATP = 4ATP mode)
Pyruvic acid is then the key product of glycolysis. What is he metabolic fate of pyruvate ? depends on the cellular need.
There are three major ways in which different cells handle pyruvic acid produced by glycolysis
(1) Lactic acid fermentation.
(2) Alcoholic fermentation.
(3) Aerobic respiration.
fermentation takes place under anaerobic conditions in many prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes.
For the complete oxidation of glucose to `CO_(2)and H_(2)O`, however, organisms adopt Kreb, cycle which is also called as aerobic respiration. This requires `O_(2)` supply.