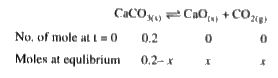A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- 20 gm of CaCO(3) is allowed to dissociate in a 5.6 litres container a...
Text Solution
|
- At a certain temperature , K(p) for dissociation of solid CaCO(3) is 4...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the solubility at 25^(@)C of CaCO(3) in a closed container c...
Text Solution
|
- When 20 g of CaCO(3) were put into 10 litre flask and heated to 800^(@...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction : CaCO(3)(s) hArr CaO(s)+CO(2)(g),K(p)=1.16atm at 800...
Text Solution
|
- At 1000K, solid carbon, CaOand CaCO(3) are mixed and allowed to atttai...
Text Solution
|
- 5 litre of a solution contains 25 mg of CaCO(3) . What is its concentr...
Text Solution
|
- Write the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of CaCO(3).
Text Solution
|
- Equilibrium constant K(p) for the reaction CaCO(3)(s) hArr CaO(s) + CO...
Text Solution
|