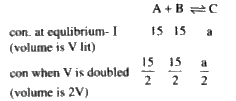
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- For , A + B hArr C. the equilibrium concentration of A and B at a temp...
Text Solution
|
- For A+B hArr C , the equilibrium concentration of A and B at a tempera...
Text Solution
|
- For gasesous reaction A+BhArrC , the equilibrium concentration of A an...
Text Solution
|
- For a reaction A+BhArr2C the equilibrium concentration of (A) and (B) ...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction : 2A + B to A2B , the rate = K[A][B]^2 with K = 2...
Text Solution
|
- For A+BhArrC, the equilibrium concentrations of A and B at a temperatu...
Text Solution
|
- For gasesous reaction A+BhArrC, the equilibrium concentration of A and...
Text Solution
|
- ఒక ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద సమతాస్థితి చార్యలో A,B ల సమతాస్థితి గాఢతలు 15 మోల్ L...
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium concentrations of A and B in the equilibrium reaction ...
Text Solution
|