Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH SERIES-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-Additional Exercise
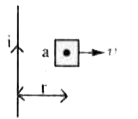
- A square loop of side a is placed in the same plane as a long straight...
Text Solution
|
- Consider Experiment II in Section 6.2. a. What would you do to obtai...
Text Solution
|
- A square loop of side 10 cm and resistance 0.5Omega is placed vertical...
Text Solution
|
- A circular coil of radius 10 cm, 500 turns and resistance 2 Omega is p...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows planar loops of different shapes moving out of or into a ...
Text Solution
|
- A closed loop is held stationary in the magnetic field between the nor...
Text Solution
|
- A metallie rod of 1 m length is rotated with a frequency of 50 revis, ...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel with 10 metallic spokes each 0.5m long is rotated with a speed...
Text Solution
|
- Two concentric circular coils, one of small radius r(1) and the other ...
Text Solution
|
- a. Obtain the expression for the magnetic energy stored in a solenoid ...
Text Solution
|
- Kamla peddles a stationary bicyle, the pedals of the bicycle are attac...
Text Solution
|