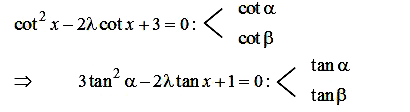A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Let alpha, beta be two real roots of the equation cot ^ 2...
Text Solution
|
- If alpha and beta are the roots of the equation x^(2)+5x-49=0, then fi...
Text Solution
|
- If alpha,beta are the roots of the equation cot^(-1)x-cot^(-1)(x+2)=15...
Text Solution
|
- Let alpha and beta be two real roots of the equation 5 cot ^(2) x- 3 c...
Text Solution
|
- Let alpha, beta be two real roots of the equation cot ^ 2...
Text Solution
|
- If sin alpha , sin beta , cos alpha in G.P., then roots of equation ...
Text Solution
|
- alpha , beta are roots of the equation lamda (x^2-x)+x+5=0 If ...
Text Solution
|
- If cot alpha cot beta=2 show that (cos(alpha+beta))/(cos(alpha-beta))...
Text Solution
|
- Let alpha and beta be two real roots of the equation 5cot^2x-3cotx-1=0...
Text Solution
|