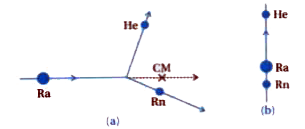
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-A HOTS|3 VideosSYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-A (TRY YOURSELF (VSQs))|94 VideosQUESTIONS ASKED IN JEE - 2020
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Question|16 VideosTHERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Question Paper (Section - D) (Answer following in brief :) Each carry 4 marks|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems