Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-B ADDITIONAL EXERCISE|12 VideosSYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-B NUMERICAL FROM .DARPAN. BASED ON TEXTBOOK|17 VideosSYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-B NUMERICALS|29 VideosQUESTIONS ASKED IN JEE - 2020
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Question|16 VideosTHERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Question Paper (Section - D) (Answer following in brief :) Each carry 4 marks|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION-SECTION-B NUMERICALS FROM TEXTUAL EXERCISE
- In the HCl molecule, the separation between the nuclei of the two atom...
Text Solution
|
- A child sits stationary at one end of a long trolley moving uniformly ...
Text Solution
|
- Show that the area of the triangle contained between the vectors veca ...
Text Solution
|
- Show that veca.(vecbxxvec c) is equal in magnitude to the volume of th...
Text Solution
|
- Find the components along the x, y, z axes of the angular momentum l o...
Text Solution
|
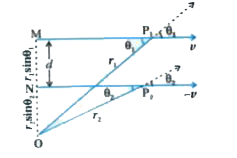
- Two particles, each of mass m and speed v, travel in opposite directio...
Text Solution
|
- A non-uniform bar of weight W is suspended at rest by two strings of n...
Text Solution
|
- A car weights 1800 kg. The distance between its front and back axles i...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Find the moment of inertia of a sphere about a tangent to the sphe...
Text Solution
|
- Torques of equal magnitude are applied to a hollow cylinder and a soli...
Text Solution
|
- A solid cylinder of mass 20 kg rotates about its axis with angular spe...
Text Solution
|
- (a) A child stands at the centre of a turntable with his two arms outs...
Text Solution
|
- A rope of negligible mass is wound round a hollow cylinder of mass 3 k...
Text Solution
|
- To maintain a rotor at a uniform angular speed of 200 rad s-1, an engi...
Text Solution
|
- From a uniform disk of radius R, a circular hole of radius R/2 is cut ...
Text Solution
|
- A metre stick is balanced on a knife edge at its centre. When two coin...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere rolls down two different inclined planes of the same he...
Text Solution
|
- A hoop of radius 2 m weights 100 kg. It rolls along a horizontal floor...
Text Solution
|
- The oxygen molecule has a mass of 5.30xx10^(-26)kg and a moment of ine...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder and a cone are of same base radius and of same height. Find...
Text Solution
|