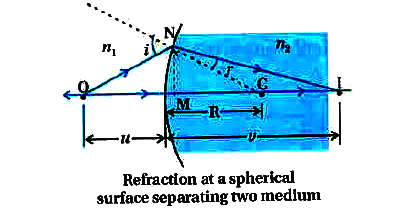
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION - A (TRY YOURSELF)|74 VideosRAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-B (NUMERICALS)(NUMERICAL FROM TEXTUAL ILLUSTRATIONS)|17 VideosMOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION D (MCQs ASKED IN COMPETITIVE EXAMS)|34 VideosSAMPLE QUESTION PAPER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise PART-B SECTION-C|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS-SECTION-D (MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs))(MCQs ASKED IN COMPETITIVE EXAMS)
- Obtain the relative between object distance and image distance in term...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is used in optical fibres ?
Text Solution
|
- An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to ….. .
Text Solution
|
- If two mirrors are kept at 60^@ to each other, then the number of imag...
Text Solution
|
- As shown in figure, a plano-convex lens of focal length 20 cm is silve...
Text Solution
|
- A light ray is incident perpendicular to one face of a 90^@ prism and ...
Text Solution
|
- A plano- convex lens of refractive index 1.5 and radius of curvature 3...
Text Solution
|
- The refractive index of transparent cylindrical rod is (2)/(root3) . A...
Text Solution
|
- A fish looking up through the water sees the outside world, contained ...
Text Solution
|
- Two point white dots are 1 mm apart on a black paper. They are viewed ...
Text Solution
|
- A thin glass (refractive index 1.5) lens has optical power of - 5D in ...
Text Solution
|
- The refractive index of glass is 1.520 for red light and 1.525 for blu...
Text Solution
|
- Two lenses of power - 15D and + 5D are in contact with each other. The...
Text Solution
|
- When monochromatic red light is used instead of blue light in a convex...
Text Solution
|
- A beaker contains water up to a height h(1) and kerosene of height h(2...
Text Solution
|
- Diameter of a plano-convex lens is 6 cm and thickness at the centre is...
Text Solution
|
- A green light is incident from the water to the air-water interface at...
Text Solution
|
- Monochromatic light is incident on a glass prism of angle A. If the re...
Text Solution
|
- On a hot summer night, the refractive index of air is smallest near th...
Text Solution
|
- An observer looks at a distant tree of height 10 m with a telescope of...
Text Solution
|
- A diverging lens with magnitude of focal length 25 cm is placed at a d...
Text Solution
|