Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-B (NUMERICALS)(NUMERICAL FROM .DARPAN. BASED ON TEXTBOOK )|12 VideosRAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-C (NCERT EXEMPLAR SOLUTION) (MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs))|16 VideosRAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-B (NUMERICALS)(NUMERICAL FROM TEXTUAL ILLUSTRATIONS)|17 VideosMOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION D (MCQs ASKED IN COMPETITIVE EXAMS)|34 VideosSAMPLE QUESTION PAPER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise PART-B SECTION-C|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS-SECTION-B (NUMERICALS)(NUMERICAL FROM TEXTUAL EXERCISE)
- An object 1.5 cm in size is placed on the side of the convex lens in t...
Text Solution
|
- At what angle should a ray of light be incident on the face of a prism...
Text Solution
|
- A card sheet divided into squares each of size 1 mm^(2) is being viewe...
Text Solution
|
- (a) At what distance should the lens be held from the figure in Exerci...
Text Solution
|
- What is the magnification in this case ?
Text Solution
|
- (a) At what distance should the lens be held from the figure in Exerci...
Text Solution
|
- What should be the distance between the object in Exercise 9.24 and th...
Text Solution
|
- Answer the following questions: (a) The angle subtended at the eye b...
Text Solution
|
- Answer the following questions: (b) In viewing through a magnifying ...
Text Solution
|
- Answer the following questions: (c) Magnifying power of a simple mic...
Text Solution
|
- Answer the following questions: (d) Why must both the objective and ...
Text Solution
|
- Answer the following questions: (e) When viewing through a compound ...
Text Solution
|
- An angular magnification (magnifying power) of 30X is desired using an...
Text Solution
|
- A small telescope has an objective lens of focal length 140cm and an e...
Text Solution
|
- For the telescope described in Exercise 9.3 (a), what is the separatio...
Text Solution
|
- If this telescope is used to view a 100 m tall tower 3 km away, what i...
Text Solution
|
- (a) For the telescope described in Exercise 9.28 (a), what is the sepa...
Text Solution
|
- A Cassegrain telescope uses two mirrors as shown in Fig. 9.30. Such a ...
Text Solution
|
- Light incident normally on a plane mirror attached to a galvanometer c...
Text Solution
|
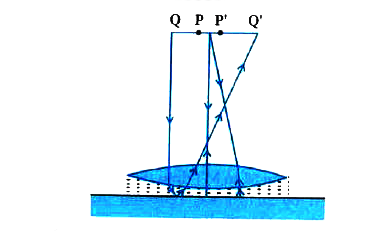
- Figure shows an equiconvex lens (of refractive index 1.50) in contact...
Text Solution
|