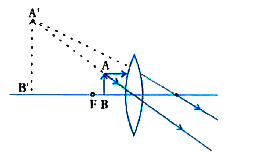
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-C (NCERT EXEMPLAR SOLUTION) (VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESITONS)|5 VideosRAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-C (NCERT EXEMPLAR SOLUTION) (SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESITONS)|6 VideosRAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-B (NUMERICALS)(NUMERICAL FROM .DARPAN. BASED ON TEXTBOOK )|12 VideosMOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION D (MCQs ASKED IN COMPETITIVE EXAMS)|34 VideosSAMPLE QUESTION PAPER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise PART-B SECTION-C|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS-SECTION-C (NCERT EXEMPLAR SOLUTION) (MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs))
- A ray of light incident at an angle theta on a refracting face of a pr...
Text Solution
|
- A short pulse of white light is incident from air to a glass slab at n...
Text Solution
|
- An object approaches a convergent lens from the left of the lens with ...
Text Solution
|
- A passenger in an aeroplane shall
Text Solution
|
- You are given four sources of light each on providing a light of a sin...
Text Solution
|
- The radius of curvature of the curved surface of a plano-convex lens i...
Text Solution
|
- The phenomena involved in the reflection of radiowaves by ionosphere i...
Text Solution
|
- The direction of ray of light incident on a concave mirror is shown by...
Text Solution
|
- The optical density of turpentine is higher than that of water while i...
Text Solution
|
- A car is moving with at a constant speed of 60 km h^(-1) on a straight...
Text Solution
|
- There are certain material developed in laboratories which have a nega...
Text Solution
|
- Consider an extended object immersed in water contained in a plane tro...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular block of glass ABCD has a refractive index 1.6. A pin is...
Text Solution
|
- Between the primary and secondary rainbows, there is a dark band known...
Text Solution
|
- A magnifying glass is used, as the object to be viewed can be brought ...
Text Solution
|
- An astronomical refractive telescope has an objective of focal length ...
Text Solution
|